Stim, ORAI and TRPC channels in the control of calcium entry signals in smooth muscle
- PMID: 18782202
- PMCID: PMC3601895
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05018.x
Stim, ORAI and TRPC channels in the control of calcium entry signals in smooth muscle
Abstract
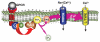
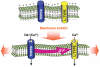
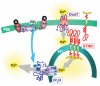
Ca2+ entry signals are crucial in the control of smooth muscle contraction. Smooth muscle cells are unusual in containing plasma membrane (PM) Ca2+ entry channels that respond to voltage changes, receptor activation and Ca2+ store depletion. Activation of these channel subtypes is highly coordinated. The TRPC6 channel, widely expressed in most smooth muscle cell types, is largely non-selective to cations and is activated by diacylglycerol arising from receptor-induced phosholipase C activation. Receptor activation results largely in Na+ ion movement through TRPC6 channels, depolarization and subsequent activation of voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ channels. The TRPC6 channels also appear to be activated by mechanical stretch, resulting again in depolarization and L-type Ca2+ channel activation. Such a coupling may be crucial in mediating the myogenic tone response in vascular smooth muscle. The emptying of stores mediated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors triggers the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ sensing protein stromal-interacting molecule (STIM) 1 to translocate into defined ER-PM junctional areas in which coupling occurs to Orai proteins, which serve as highly Ca2+-selective low-conductance Ca2+ entry channels. These ER-PM junctional domains may serve as crucial sites of interaction and integration between the function of store-operated, receptor-operated and voltage-operated Ca2+ channels. The STIM, Orai and TRPC channels represent highly promising new pharmacological targets through which such control may be induced.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Store-Operated Calcium Entry in Müller Glia Is Controlled by Synergistic Activation of TRPC and Orai Channels.J Neurosci. 2016 Mar 16;36(11):3184-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4069-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26985029 Free PMC article.
-
Remodelling of the endoplasmic reticulum during store-operated calcium entry.Biol Cell. 2011 Aug;103(8):365-80. doi: 10.1042/BC20100152. Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21736554 Review.
-
TRPC channels function independently of STIM1 and Orai1.J Physiol. 2009 May 15;587(Pt 10):2275-98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.170431. Epub 2009 Mar 30. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19332491 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential channels in human platelets: expression and functional role.Curr Mol Med. 2012 Dec;12(10):1319-28. doi: 10.2174/156652412803833616. Curr Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22834833 Review.
-
Human umbilical artery smooth muscle exhibits a 2-APB-sensitive capacitative contractile response evoked by vasoactive substances and expresses mRNAs for STIM, Orai and TRPC channels.Biocell. 2012 Aug;36(2):73-81. Biocell. 2012. PMID: 23185782
Cited by
-
STIM proteins: integrators of signalling pathways in development, differentiation and disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Jul;14(7):1890-903. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01097.x. Epub 2010 Jun 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20561111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Celastrol inhibits store operated calcium entry and suppresses psoriasis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1111798. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1111798. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36817139 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-dependent reactive oxygen species signaling in the pulmonary circulation: focus on ion channels.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Feb 20;22(6):537-52. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6234. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 25545236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebral Autoregulation in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Front Neurol. 2021 Jul 23;12:688362. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.688362. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34367053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+-stores in sperm: their identities and functions.Reproduction. 2009 Sep;138(3):425-37. doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0134. Epub 2009 Jun 19. Reproduction. 2009. PMID: 19542252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: Dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:517–29. - PubMed
-
- Clapham DE. Calcium signaling. Cell. 2007;131:1047–58. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Jaggar JH, Porter VA, Lederer WJ, Nelson MT. Calcium sparks in smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000;278:C235–56. - PubMed
-
- Venkatachalam K, van Rossum DB, Patterson RL, Ma HT, Gill DL. The cellular and molecular basis of store-operated calcium entry. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:E263–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

