Effect of proteolytic activity of Epicoccum purpurascens major allergen, Epi p 1 in allergic inflammation
- PMID: 18782325
- PMCID: PMC2612722
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03762.x
Effect of proteolytic activity of Epicoccum purpurascens major allergen, Epi p 1 in allergic inflammation
Abstract
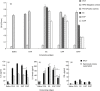
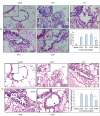
Enzymes play an important role in inducing airway inflammation, but knowledge is limited to few proteins. This study was carried out to assess the role of Epi p 1, a serine protease of Epicoccum purpurascens, in inducing allergy and inflammation in a murine model. Balb/c mice were sensitized with Epi p 1 active protease (EAP) or Epicoccum extract. Subsequently, Epi p 1 sensitized mice were boosted on day 14 with EAP or inactivated protease (EIAP). Three intranasal challenges were given and mice were killed to obtain blood, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), spleen and lung tissues. Cellular airways infiltration, immunoglobulin E (Ig)E titres and cytokine levels in BALF and splenocyte culture supernatant were compared. Mice immunized with EAP had higher Epi p 1-specific serum IgE and IgG1 than EIAP immunized mice (P < 0.01). There was a twofold difference in the number of eosinophils in BALF of EAP mice and EIAP mice (P < 0.01). A similar trend was recorded for eosinophil peroxidase activity (P < 0.05), indicating the role of proteolytic activity in inducing inflammation. Further, lung histology revealed increased leucocyte infiltration and airway narrowing, with higher inflammation scores in the EAP group than in the EIAP group. The lungs of EAP mice showed increased mucus and goblet cell metaplasia. Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-5 levels were higher in BALF and splenocyte culture supernatant of EAP mice than in EIAP mice (P < 0.05), indicating a T helper 2 response. Proteolytic activity of Epi p 1 plays an important role in inducing allergic inflammation. The enzymatically inactive form may be investigated for immunotherapy.
Figures
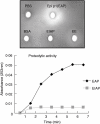
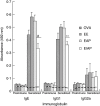
 ) shows the values of saline control in each group. Statistical significance between specific IgE/IgG1 of EAP and EIAP sensitized mice is mentioned as P-value (at a confidence level of 0·05); #P < 0·005; **P < 0·01. Data are presented as ± s.d.
) shows the values of saline control in each group. Statistical significance between specific IgE/IgG1 of EAP and EIAP sensitized mice is mentioned as P-value (at a confidence level of 0·05); #P < 0·005; **P < 0·01. Data are presented as ± s.d.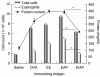
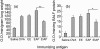
References
-
- Jeong SK, Kim HJ, Youm JK, et al. Mite and cockroach allergens activate protease activated receptor-2 and delay epidermal permeability barrier recovery. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:1930–9. - PubMed
-
- Runswick S, Mitchell T, Davies P, Robinson C, Garrod DR. Pollen proteolytic enzymes degrade tight junctions. Respirology. 2007;12:834–42. - PubMed
-
- Shen HD, Tam MF, Tang RB, Chou H. Aspergillus and Penicillium allergens: focus on proteases. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2007;7:351–6. - PubMed
-
- Ghaemmaghami AM, Gough L, Sewell HF, Shakib F. The proteolytic activity of the major dust mite allergen Der p 1 conditions dendritic cells to produce less interleukin-12: allergen-induced Th2 bias determined at the dendritic cell level. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002;32:1468–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

