Multiple MyD88-dependent responses contribute to pulmonary clearance of Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 18782351
- PMCID: PMC2752851
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01234.x
Multiple MyD88-dependent responses contribute to pulmonary clearance of Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
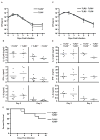
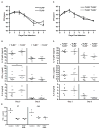
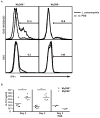
MyD88-dependent signalling is important for secretion of early inflammatory cytokines and host protection in response to Legionella pneumophila infection. Although toll-like receptor (TLR)2 contributes to MyD88-dependent clearance of L. pneumophila, TLR-independent functions of MyD88 could also be important. To determine why MyD88 is critical for host protection to L. pneumophila, the contribution of multiple TLRs and IL-18 receptor (IL-18R)-dependent interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production in a mouse was examined. Mice deficient for TLR5 or TLR9, or deficient for TLR2 along with either TLR5 or TLR9, were competent for controlling bacterial replication and had no apparent defects in cytokine production compared with control mice. MyD88-dependent production of IFN-gamma in the lung was mediated primarily by natural killer cells and required IL-18R signalling. Reducing IFN-gamma levels did not greatly affect the kinetics of L. pneumophila replication or clearance in infected mice. Additionally, IFN-gamma-deficient mice did not have a susceptibility phenotype as severe as the MyD88-deficient mice and were able to control a pulmonary infection by L. pneumophila. Thus, MyD88-dependent innate immune responses induced by L. pneumophila involve both TLR-dependent responses and IL-18R-dependent production of IFN-gamma by natural killer cells, and these MyD88-dependent pathways can function independently to provide host protection against an intracellular pathogen.
Figures
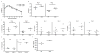


References
-
- Adachi O, Kawai T, Takeda K, Matsumoto M, Tsutsui H, Sakagami M, et al. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity. 1998;9:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Amer A, Franchi L, Kanneganti TD, Body-Malapel M, Ozoren N, Brady G, et al. Regulation of Legionella phagosome maturation and infection through flagellin and host Ipaf. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:35217–35223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

