4-Hydroxynonenal induces apoptosis in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes: the protective role of glutathione-S-transferase
- PMID: 18782442
- PMCID: PMC2592788
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2503
4-Hydroxynonenal induces apoptosis in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes: the protective role of glutathione-S-transferase
Abstract
Introduction: 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) is one of the most abundant and reactive aldehydes of lipid peroxidation products and exerts various effects on intracellular and extracellular signalling cascades. We have previously shown that HNE at low concentrations could be considered as an important mediator of catabolic and inflammatory processes in osteoarthritis (OA). In the present study, we focused on characterizing the signalling cascade induced by high HNE concentration involved in cell death in human OA chondrocytes.
Methods: Markers of apoptosis were quantified with commercial kits. Protein levels were evaluated by Western blotting. Glutathione (GSH) and ATP levels were measured with commercial kits. Glucose uptake was assessed by 2-deoxy-D-[3H]-glucose. The role of GSH-S-transferase A4-4 (GSTA4-4) in controlling HNE-induced chondrocyte apoptosis was investigated by chondrocyte transfection with small interfering RNA (siRNA) or with the expression vector of GSTA4-4.
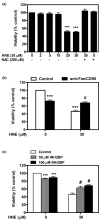
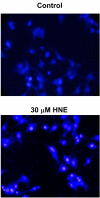
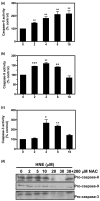
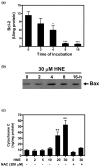
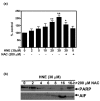
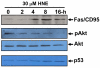
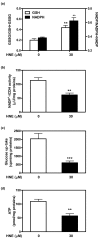
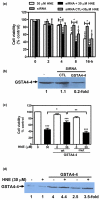
Results: Our data showed that HNE at concentrations of up to 10 microM did not alter cell viability but was cytotoxic at concentrations of greater than or equal to 20 microM. HNE-induced chondrocyte death exhibited several classical hallmarks of apoptosis, including caspase activation, cytochrome c and apoptosis-induced factor release from mitochondria, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage, Bcl-2 downregulation, Bax upregulation, and DNA fragmentation. Our study of signalling pathways revealed that HNE suppressed pro-survival Akt kinase activity but, in contrast, induced Fas/CD95 and p53 expression in chondrocytes. All of these effects were inhibited by an antioxidant, N-acetyl-cysteine. Analysis of cellular energy and redox status showed that HNE induced ATP, NADPH, and GSH depletion and inhibited glucose uptake and citric acid cycle activity. GSTA4-4 ablation by the siRNA method augmented HNE cytotoxicity, but, conversely, its overexpression efficiently protected chondrocytes from HNE-induced cell death.
Conclusion: Our study provides novel insights into the potential mechanisms of cell death in OA cartilage and suggests the potential role of HNE in OA pathophysiology. GSTA4-4 expression is critically important for cellular defence against oxidative stress-induced cell death in OA cartilage, possibly by HNE elimination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase prevents lipid peroxidation in osteoarthritic chondrocytes.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Jul;113(7):2256-67. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24096. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22573548
-
4-hydroxynonenal induces mitochondrial oxidative stress, apoptosis and expression of glutathione S-transferase A4-4 and cytochrome P450 2E1 in PC12 cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006 Oct 15;216(2):309-18. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.06.001. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16843508
-
Differential regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase by 4-hydroxynonenal in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes through ATF-2/CREB-1 transactivation and concomitant inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling cascade.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Apr 1;100(5):1217-31. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21110. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17031850
-
Lipid peroxidation and cell cycle signaling: 4-hydroxynonenal, a key molecule in stress mediated signaling.Acta Biochim Pol. 2003;50(2):319-36. Acta Biochim Pol. 2003. PMID: 12833161 Review.
-
Regulation of 4-hydroxynonenal-mediated signaling by glutathione S-transferases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2004 Sep 1;37(5):607-19. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.05.033. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15288119 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic iron reduction via an iron deficient diet decreases the severity of knee cartilage lesions in the Dunkin-Hartley guinea pig model of osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022 Nov;30(11):1482-1494. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2022.08.007. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022. PMID: 36030059 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of glutathione transferases with 4-hydroxynonenal.Drug Metab Rev. 2011 May;43(2):165-78. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2011.558092. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Drug Metab Rev. 2011. PMID: 21401344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALDOSE REDUCTASE: New Insights for an Old Enzyme.Biomol Concepts. 2011 Apr 1;2(1-2):103-114. doi: 10.1515/BMC.2011.002. Biomol Concepts. 2011. PMID: 21547010 Free PMC article.
-
The role of resolvin D1 in the regulation of inflammatory and catabolic mediators in osteoarthritis.Inflamm Res. 2016 Aug;65(8):635-45. doi: 10.1007/s00011-016-0946-x. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Inflamm Res. 2016. PMID: 27056390
-
Lipid peroxidation in osteoarthritis: focusing on 4-hydroxynonenal, malondialdehyde, and ferroptosis.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Aug 29;9(1):320. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01613-9. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37644030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim HA, Lee YJ, Seong SC, Choe KW, Song YW. Apoptotic chondrocyte death in human osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:455–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

