Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase activity affects growth and riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii
- PMID: 18782443
- PMCID: PMC2551608
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-8-67
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase activity affects growth and riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii
Abstract
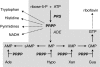
Background: Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a central compound for cellular metabolism and may be considered as a link between carbon and nitrogen metabolism. PRPP is directly involved in the de novo and salvage biosynthesis of GTP, which is the immediate precursor of riboflavin. The industrial production of this vitamin using the fungus Ashbya gossypii is an important biotechnological process that is strongly influenced by substrate availability.
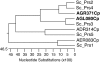
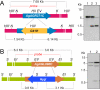
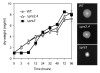
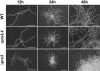
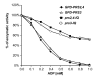
Results: Here we describe the characterization and manipulation of two genes of A. gossypii encoding PRPP synthetase (AGR371C and AGL080C). We show that the AGR371C and AGL080C gene products participate in PRPP synthesis and exhibit inhibition by ADP. We also observed a major contribution of AGL080C to total PRPP synthetase activity, which was confirmed by an evident growth defect of the Deltaagl080c strain. Moreover, we report the overexpression of wild-type and mutant deregulated isoforms of Agr371cp and Agl080cp that significantly enhanced the production of riboflavin in the engineered A. gossypii strains.
Conclusion: It is shown that alterations in PRPP synthetase activity have pleiotropic effects on the fungal growth pattern and that an increase in PRPP synthetase enzymatic activity can be used to enhance riboflavin production in A. gossypii.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic engineering of the purine pathway for riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Oct;71(10):5743-51. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.10.5743-5751.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16204483 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological characterization of a pyrimidine auxotroph exposes link between uracil phosphoribosyltransferase regulation and riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii.N Biotechnol. 2019 May 25;50:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2018.12.004. Epub 2018 Dec 24. N Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30590201
-
New biotechnological applications for Ashbya gossypii: Challenges and perspectives.Bioengineered. 2017 Jul 4;8(4):309-315. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2016.1234543. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Bioengineered. 2017. PMID: 27791453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic flux analysis in Ashbya gossypii using 13C-labeled yeast extract: industrial riboflavin production under complex nutrient conditions.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Oct 16;17(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-1003-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 30326916 Free PMC article.
-
[Increased activity of PRPP synthetase].Nihon Rinsho. 2008 Apr;66(4):694-8. Nihon Rinsho. 2008. PMID: 18409517 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Guanine nucleotide binding to the Bateman domain mediates the allosteric inhibition of eukaryotic IMP dehydrogenases.Nat Commun. 2015 Nov 12;6:8923. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9923. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26558346 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of two aptamers with differing ligand specificity reveal ruggedness in the functional landscape of RNA.Elife. 2018 Jun 7;7:e36381. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36381. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29877798 Free PMC article.
-
Production of riboflavin and related cofactors by biotechnological processes.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Feb 13;19(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01302-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 32054466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of riboflavin.Microb Cell Fact. 2014 Jul 16;13:104. doi: 10.1186/s12934-014-0104-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2014. PMID: 25027702 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of xylose by engineered strains of Ashbya gossypii for the production of microbial oils.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 Jan 3;10:3. doi: 10.1186/s13068-016-0685-9. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 28053663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vandamme EJ. Production of vitamins, coenzymes and related biochemicals by biotechnological processes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 1992;53:313–327. - PubMed
-
- Stahmann KP, Arst HN, Jr, Althofer H, Revuelta JL, Monschau N, Schlupen C, Gatgens C, Wiesenburg A, Schlosser T. Riboflavin, overproduced during sporulation of Ashbya gossypii, protects its hyaline spores against ultraviolet light. Environ Microbiol. 2001;3:545–550. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2001.00225.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Revuelta JL, Buitrago MJ, Santos MA. Riboflavin-biosynthesis in fungi. Patent nr WO9526406 In, C12N15/52 edn: BASF AG (DE) 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

