X-ray crystal structure of a TRPM assembly domain reveals an antiparallel four-stranded coiled-coil
- PMID: 18782578
- PMCID: PMC2630241
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.059
X-ray crystal structure of a TRPM assembly domain reveals an antiparallel four-stranded coiled-coil
Abstract
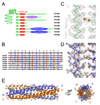
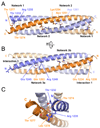
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels comprise a large family of tetrameric cation-selective ion channels that respond to diverse forms of sensory input. Earlier studies showed that members of the TRPM subclass possess a self-assembling tetrameric C-terminal cytoplasmic coiled-coil domain that underlies channel assembly and trafficking. Here, we present the high-resolution crystal structure of the coiled-coil domain of the channel enzyme TRPM7. The crystal structure, together with biochemical experiments, reveals an unexpected four-stranded antiparallel coiled-coil architecture that bears unique features relative to other antiparallel coiled-coils. Structural analysis indicates that a limited set of interactions encode assembly specificity determinants and uncovers a previously unnoticed segregation of TRPM assembly domains into two families that correspond with the phylogenetic divisions seen for the complete subunits. Together, the data provide a framework for understanding the mechanism of TRPM channel assembly and highlight the diversity of forms found in the coiled-coil fold.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Coiled coils direct assembly of a cold-activated TRP channel.Neuron. 2006 Jul 20;51(2):201-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.06.023. Neuron. 2006. PMID: 16846855 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a trimeric form of the K(V)7.1 (KCNQ1) A-domain tail coiled-coil reveals structural plasticity and context dependent changes in a putative coiled-coil trimerization motif.Protein Sci. 2009 Oct;18(10):2100-14. doi: 10.1002/pro.224. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19693805 Free PMC article.
-
The region adjacent to the C-end of the inner gate in transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) channels plays a central role in allosteric channel activation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 10;289(41):28579-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.577478. Epub 2014 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25157108 Free PMC article.
-
A structural overview of the ion channels of the TRPM family.Cell Calcium. 2020 Jan;85:102111. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102111. Epub 2019 Nov 24. Cell Calcium. 2020. PMID: 31812825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subunit interaction in channel assembly and functional regulation of transient receptor potential melastatin (TRPM) channels.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Feb;35(Pt 1):86-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0350086. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17233608 Review.
Cited by
-
The coiled-coil domain of zebrafish TRPM7 regulates Mg·nucleotide sensitivity.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 15;6:33459. doi: 10.1038/srep33459. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27628598 Free PMC article.
-
The cytoplasmic coiled-coil mediates cooperative gating temperature sensitivity in the voltage-gated H(+) channel Hv1.Nat Commun. 2012 May 8;3:816. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1823. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 22569364
-
TRPM3_miR-204: a complex locus for eye development and disease.Hum Genomics. 2020 Feb 18;14(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40246-020-00258-4. Hum Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32070426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligomeric state of purified transient receptor potential melastatin-1 (TRPM1), a protein essential for dim light vision.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 26;289(39):27019-27033. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.593780. Epub 2014 Aug 11. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25112866 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Mg2+-sensitive ORF in the 5'-leader of TRPM7 magnesium channel mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Nov 10;42(20):12779-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku951. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25326319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clapham DE. TRP channels as cellular sensors. Nature. 2003;426:517–524. - PubMed
-
- Julius D, Basbaum AI. Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature. 2001;413:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Hille B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes. 3rd edit. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, Inc.; 2001.
-
- Yu FH, Catterall WA. The VGL-chanome: a protein superfamily specialized for electrical signaling and ionic homeostasis. Sci STKE 2004. 2004:re15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

