Biogeography of the fauna of French Polynesia: diversification within and between a series of hot spot archipelagos
- PMID: 18782725
- PMCID: PMC2607382
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0124
Biogeography of the fauna of French Polynesia: diversification within and between a series of hot spot archipelagos
Abstract
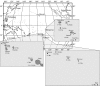
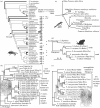
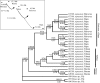
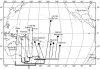
The islands of French Polynesia cover an area the size of Europe, though total land area is smaller than Rhode Island. Each hot spot archipelago (Societies, Marquesas, Australs) is chronologically arranged. With the advent of molecular techniques, relatively precise estimations of timing and source of colonization have become feasible. We compile data for the region, first examining colonization (some lineages dispersed from the west, others from the east). Within archipelagos, blackflies (Simulium) provide the best example of adaptive radiation in the Societies, though a similar radiation occurs in weevils (Rhyncogonus). Both lineages indicate that Tahiti hosts the highest diversity. The more remote Marquesas show clear examples of adaptive radiation in birds, arthropods and snails. The Austral Islands, though generally depauperate, host astonishing diversity on the single island of Rapa, while lineages on other islands are generally widespread but with large genetic distances between islands. More recent human colonization has changed the face of Polynesian biogeography. Molecular markers highlight the rapidity of Polynesian human (plus commensal) migrations and the importance of admixture from other populations during the period of prehistoric human voyages. However, recent increase in traffic has brought many new, invasive species to the region, with the future of the indigenous biota uncertain.
Figures
References
-
- Adamson A.M. Marquesan insects: environment. Bernice P. Bishop Mus. Bull. 1936;139:1–73.
-
- Adamson A.M. Review of the fauna of the Marquesas Islands and discussion of its origin. Bernice P. Bishop Mus. Bull. 1939;159:1–93.
-
- Arnedo M.A, Gillespie R.G. Species diversification patterns in the Polynesian jumping spider genus Havaika Proszynski 2001 (Araneae, Salticidae) Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006;41:472–495. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.05.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Austin C.C. Lizards took express train to Polynesia. Nature. 1999;397:113–114. doi:10.1038/16365 - DOI
-
- Beadell J.S, et al. Global phylogeographic limits of Hawaii's avian malaria. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2006;273:2935–2944. doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3671 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

