Human alpha-defensins inhibit BK virus infection by aggregating virions and blocking binding to host cells
- PMID: 18782756
- PMCID: PMC2576552
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M805902200
Human alpha-defensins inhibit BK virus infection by aggregating virions and blocking binding to host cells
Abstract
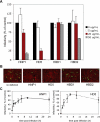
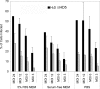
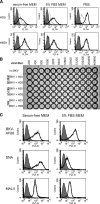
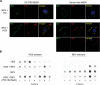
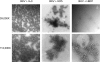
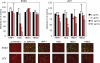
BK virus (BKV) is a polyomavirus that establishes a lifelong persistence in most humans and is a major impediment to success of kidney grafts. The function of the innate immune system in BKV infection and pathology has not been investigated. Here we examine the role of antimicrobial defensins in BKV infection of Vero cells. Our data show that alpha-defensin human neutrophil protein 1 (HNP1) and human alpha-defensin 5 (HD5) inhibit BKV infection by targeting an early event in the viral lifecycle. HD5 treatment of BKV reduced viral attachment to cells, whereas cellular treatment with HD5 did not. Colocalization studies indicated that HD5 interacts directly with BKV. Ultrastructural analysis revealed HD5-induced aggregation of virions. HD5 also inhibited infection of cells by other related polyomaviruses. This is the first study to demonstrate polyomavirus sensitivity to defensins. We also show a novel mechanism whereby HD5 binds to BKV leading to aggregation of virion particles preventing normal virus binding to the cell surface and uptake into cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Agnoprotein Is an Essential Egress Factor during BK Polyomavirus Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 19;19(3):902. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030902. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29562663 Free PMC article.
-
Human Defensins Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Blocking Viral Entry.Viruses. 2021 Jun 26;13(7):1246. doi: 10.3390/v13071246. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34206990 Free PMC article.
-
The human alpha defensin HD5 neutralizes JC polyomavirus infection by reducing endoplasmic reticulum traffic and stabilizing the viral capsid.J Virol. 2014 Jan;88(2):948-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02766-13. Epub 2013 Nov 6. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24198413 Free PMC article.
-
Update on BK virus entry and intracellular trafficking.Transpl Infect Dis. 2006 Jun;8(2):62-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3062.2006.00153.x. Transpl Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16734628 Review.
-
The Function and Modification of Human Defensin 5.Protein Pept Lett. 2023;30(10):830-840. doi: 10.2174/0109298665252235230919071229. Protein Pept Lett. 2023. PMID: 37861034 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifaceted mechanisms of HIV-1 entry inhibition by human α-defensin.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):28821-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.375949. Epub 2012 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22733823 Free PMC article.
-
α-Defensin HD5 Stabilizes Human Papillomavirus 16 Capsid/Core Interactions.Pathog Immun. 2019 Sep 12;4(2):196-234. doi: 10.20411/pai.v4i2.314. eCollection 2019. Pathog Immun. 2019. PMID: 31583330 Free PMC article.
-
Defending the fort: a role for defensin-2 in limiting Rickettsia montanensis infection of Dermacentor variabilis.Insect Mol Biol. 2014 Aug;23(4):457-65. doi: 10.1111/imb.12094. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Insect Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24779891 Free PMC article.
-
Human Defensins: Structure, Function, and Potential as Therapeutic Antimicrobial Agents with Highlights Against SARS CoV-2.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jun;17(3):1563-1583. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10436-8. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39693007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral Activities of Human Host Defense Peptides.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(9):1420-1443. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190805151654. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31385762 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shah, K. V., Daniel, R. W., and Strandberg, J. D. (1975) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 54 945-950 - PubMed
-
- Knowles, W. A., Pipkin, P., Andrews, N., Vyse, A., Minor, P., Brown, D. W., and Miller, E. (2003) J. Med. Virol. 71 115-123 - PubMed
-
- Heritage, J., Chesters, P. M., and McCance, D. J. (1981) J. Med. Virol. 8 143-150 - PubMed
-
- Arthur, R. R., Shah, K. V., Charache, P., and Saral, R. (1988) J. Infect. Dis. 158 563-569 - PubMed
-
- Rosen, S., Harmon, W., Krensky, A. M., Edelson, P. J., Padgett, B. L., Grinnell, B. W., Rubino, M. J., and Walker, D. L. (1983) N. Engl. J. Med. 308 1192-1196 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

