SUMOylation regulates nuclear localization of Krüppel-like factor 5
- PMID: 18782761
- PMCID: PMC2581587
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M803612200
SUMOylation regulates nuclear localization of Krüppel-like factor 5
Abstract
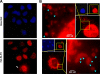
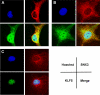
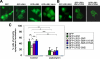
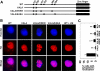
SUMOylation is a form of post-translational modification shown to control nuclear transport. Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) is an important mediator of cell proliferation and is primarily localized to the nucleus. Here we show that mouse KLF5 is SUMOylated at lysine residues 151 and 202. Mutation of these two lysines or two conserved nearby glutamates results in the loss of SUMOylation and increased cytoplasmic distribution of KLF5, suggesting that SUMOylation enhances nuclear localization of KLF5. Lysine 151 is adjacent to a nuclear export signal (NES) that resembles a consensus NES. The NES in KLF5 directs a fused green fluorescence protein to the cytoplasm, binds the nuclear export receptor CRM1, and is inhibited by leptomycin and site-directed mutagenesis. SUMOylation facilitates nuclear localization of KLF5 by inhibiting this NES activity, and enhances the ability of KLF5 to stimulate anchorage-independent growth of HCT116 colon cancer cells. A survey of proteins whose nuclear localization is regulated by SUMOylation reveals that SUMOylation sites are frequently located in close proximity to NESs. A relatively common mechanism for SUMOylation to regulate nucleocytoplasmic transport may lie in the interplay between neighboring NES and SUMOylation motifs.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Protein inhibitor of activated STAT1 interacts with and up-regulates activities of the pro-proliferative transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 5.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 16;282(7):4782-4793. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603413200. Epub 2006 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17178721 Free PMC article.
-
p53 SUMOylation promotes its nuclear export by facilitating its release from the nuclear export receptor CRM1.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Sep;24(17):2739-52. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-10-0771. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23825024 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction of the Ras effector RASSF5 with the tyrosine kinase Lck: critical role in nucleocytoplasmic transport and cell cycle regulation.J Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 19;397(1):89-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Jan 11. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20064523
-
Nucleo-cytoplasmic localization domains regulate Krüppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) protein stability and tumor suppressor function.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 9;5(9):e12639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012639. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20844588 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO and Nucleocytoplasmic Transport.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;963:111-126. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50044-7_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28197909 Review.
Cited by
-
New insights into KLFs and SOXs in cancer pathogenesis, stemness, and therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2023 May;90:29-44. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.02.003. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023. PMID: 36806560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of selective ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like protease inhibitors using a fluorescence-based multiplex assay format.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2011 Apr;9(2):165-73. doi: 10.1089/adt.2010.0317. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2011. PMID: 21133675 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of SUMO in Metabolic Regulation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;963:143-168. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50044-7_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28197911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current knowledge of Krüppel-like factor 5 and vascular remodeling: providing insights for therapeutic strategies.J Mol Cell Biol. 2021 May 7;13(2):79-90. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjaa080. J Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33493334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Krüppel traffic report: cooperative signals direct KLF8 nuclear transport.Cell Res. 2009 Sep;19(9):1041-3. doi: 10.1038/cr.2009.103. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19727130 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Johnson, E. S. (2004) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73 355-382 - PubMed
-
- Wilson, V. G., and Rangasamy, D. (2001) Exp. Cell Res. 271 57-65 - PubMed
-
- Pichler, A., and Melchior, F. (2002) Traffic 3 381-387 - PubMed
-
- Terry, L. J., Shows, E. B., and Wente, S. R. (2007) Science 318 1412-1416 - PubMed
-
- Pemberton, L. F., and Paschal, B. M. (2005) Traffic 6 187-198 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

