Identification of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase, a key enzyme removing cholesterol from macrophages
- PMID: 18782767
- PMCID: PMC2662263
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M802686200
Identification of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase, a key enzyme removing cholesterol from macrophages
Abstract
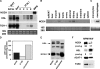
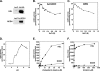
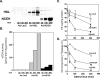
Unstable lipid-rich plaques in atherosclerosis are characterized by the accumulation of macrophage foam cells loaded with cholesterol ester (CE). Although hormone-sensitive lipase and cholesteryl ester hydrolase (CEH) have been proposed to mediate the hydrolysis of CE in macrophages, circumstantial evidence suggests the presence of other enzymes with neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase (nCEH) activity. Here we show that the murine orthologue of KIAA1363, designated as neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase (NCEH), is a microsomal nCEH with high expression in murine and human macrophages. The effect of various concentrations of NaCl on its nCEH activity resembles that on endogenous nCEH activity of macrophages. RNA silencing of NCEH decreases nCEH activity at least by 50%; conversely, its overexpression inhibits the CE formation in macrophages. Immunohistochemistry reveals that NCEH is expressed in macrophage foam cells in atherosclerotic lesions. These data indicate that NCEH is responsible for a major part of nCEH activity in macrophages and may be a potential therapeutic target for the prevention of atherosclerosis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hormone-sensitive lipase overexpression increases cholesteryl ester hydrolysis in macrophage foam cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998 Jun;18(6):991-8. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.6.991. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9633942
-
The role of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolysis in macrophage foam cells.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2011;18(5):359-64. doi: 10.5551/jat.7013. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2011. PMID: 21467808 Review.
-
Ablation of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 accelerates atherosclerosis.Cell Metab. 2009 Sep;10(3):219-28. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.08.004. Cell Metab. 2009. PMID: 19723498
-
Low level expression of hormone-sensitive lipase in arterial macrophage-derived foam cells: potential explanation for low rates of cholesteryl ester hydrolysis.Atherosclerosis. 2000 Apr;149(2):343-50. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(99)00345-7. Atherosclerosis. 2000. PMID: 10729384
-
Early steps in reverse cholesterol transport: cholesteryl ester hydrolase and other hydrolases.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012 Apr;19(2):136-41. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e3283507836. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012. PMID: 22262001 Review.
Cited by
-
ISG15 Is a Novel Regulator of Lipid Metabolism during Vaccinia Virus Infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0389322. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03893-22. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36453897 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Role of SREBP-1c Large-VLDL Pathway in Environment-Induced Hypertriglyceridemia of Apo AV Deficiency.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019 Mar;39(3):373-386. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311931. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30700132 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcal serum opacity factor promotes cholesterol ester metabolism and bile acid secretion in vitro and in vivo.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Mar;1861(3):196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.12.006. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26709142 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 (NCEH1) impairs endothelial function in diet-induced diabetic mice.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Apr 25;23(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02239-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38664801 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase 1 in cholesteryl ester hydrolysis in murine macrophages.J Lipid Res. 2014 Oct;55(10):2033-40. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M047787. Epub 2014 May 27. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24868095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fuster, V., Moreno, P. R., Fayad, Z. A., Corti, R., and Badimon, J. J. (2005) J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 46 937-954 - PubMed
-
- Greaves, D. R., and Gordon, S. (2005) J. Lipid Res. 46 11-20 - PubMed
-
- Chang, T. Y., Chang, C. C., Ohgami, N., and Yamauchi, Y. (2006) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 22 129-157 - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. S., Ho, Y. K., and Goldstein, J. L. (1980) J. Biol. Chem. 255 9344-9352 - PubMed
-
- Oram, J. F., and Vaughan, A. M. (2006) Circ. Res. 99 1031-1043 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

