Obscurin targets ankyrin-B and protein phosphatase 2A to the cardiac M-line
- PMID: 18782775
- PMCID: PMC2581558
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806050200
Obscurin targets ankyrin-B and protein phosphatase 2A to the cardiac M-line
Abstract
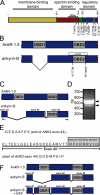
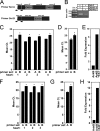
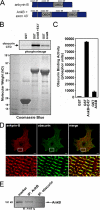
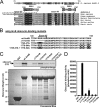
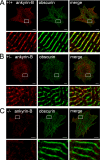
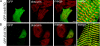
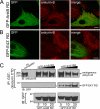
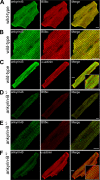
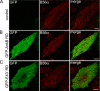
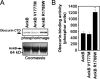
Ankyrin-B targets ion channels and transporters in excitable cells. Dysfunction in ankyrin-B-based pathways results in defects in cardiac physiology. Despite a wealth of knowledge regarding the role of ankyrin-B for cardiac function, little is known regarding the mechanisms underlying ankyrin-B regulation. Moreover, the pathways underlying ankyrin-B targeting in heart are unclear. We report that alternative splicing regulates ankyrin-B localization and function in cardiomyocytes. Specifically, we identify a novel exon (exon 43') in the ankyrin-B regulatory domain that mediates interaction with the Rho-GEF obscurin. Ankyrin-B transcripts harboring exon 43' represent the primary cardiac isoform in human and mouse. We demonstrate that ankyrin-B and obscurin are co-localized at the M-line of myocytes and co-immunoprecipitate from heart. We define the structural requirements for ankyrin-B/obscurin interaction to two motifs in the ankyrin-B regulatory domain and demonstrate that both are critical for obscurin/ankyrin-B interaction. In addition, we demonstrate that interaction with obscurin is required for ankyrin-B M-line targeting. Specifically, both obscurin-binding motifs are required for the M-line targeting of a GFP-ankyrin-B regulatory domain. Moreover, this construct acts as a dominant-negative by competing with endogenous ankyrin-B for obscurin-binding at the M-line, thus providing a powerful new tool to evaluate the function of obscurin/ankyrin-B interactions. With this new tool, we demonstrate that the obscurin/ankyrin-B interaction is critical for recruitment of PP2A to the cardiac M-line. Together, these data provide the first evidence for the molecular basis of ankyrin-B and PP2A targeting and function at the cardiac M-line. Finally, we report that ankyrin-B R1788W is localized adjacent to the ankyrin-B obscurin-binding motif and increases binding activity for obscurin. In summary, our new findings demonstrate that ANK2 is subject to alternative splicing that gives rise to unique polypeptides with diverse roles in cardiac function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Binding of an ankyrin-1 isoform to obscurin suggests a molecular link between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils in striated muscles.J Cell Biol. 2003 Jan 20;160(2):245-53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200208109. Epub 2003 Jan 13. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12527750 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular interactions with obscurin are involved in the localization of muscle-specific small ankyrin1 isoforms to subcompartments of the sarcoplasmic reticulum.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Nov 1;312(18):3546-58. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.07.027. Epub 2006 Aug 16. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16962094
-
Obscurin regulates ankyrin macromolecular complex formation.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022 Jul;168:44-57. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.04.008. Epub 2022 Apr 18. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35447147 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac ankyrins: Essential components for development and maintenance of excitable membrane domains in heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2006 Jul 1;71(1):22-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.03.018. Epub 2006 Mar 28. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. PMID: 16650839 Review.
-
Cardiac ankyrins in health and disease.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009 Aug;47(2):203-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.04.010. Epub 2009 Apr 24. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19394342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Obscurin and SPEG Kinase Biology.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 2;10(5):984. doi: 10.3390/jcm10050984. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33801198 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic transcriptome and histomorphology analysis of developmental traits of hindlimb thigh muscle from Odorrana tormota and its adaptability to different life history stages.BMC Genomics. 2021 May 20;22(1):369. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07677-0. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34016051 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the molecular basis of cardiomyopathy.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Feb 1;322(2):H181-H233. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00562.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34797172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein phosphatase 2A is crucial for sarcomere organization in Caenorhabditis elegans striated muscle.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Aug 15;29(17):2084-2097. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-03-0192. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29949401 Free PMC article.
-
Ankyrin-B regulates Cav2.1 and Cav2.2 channel expression and targeting.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 21;289(8):5285-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.523639. Epub 2014 Jan 6. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24394417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohler, P. J., Schott, J. J., Gramolini, A. O., Dilly, K. W., Guatimosim, S., duBell, W. H., Song, L. S., Haurogne, K., Kyndt, F., Ali, M. E., Rogers, T. B., Lederer, W. J., Escande, D., Le Marec, H., and Bennett, V. (2003) Nature 421 634-639 - PubMed
-
- Mohler, P. J., Le Scouarnec, S., Denjoy, I., Lowe, J. S., Guicheney, P., Caron, L., Driskell, I. M., Schott, J. J., Norris, K., Leenhardt, A., Kim, R. B., Escande, D., and Roden, D. M. (2007) Circulation 115 432-441 - PubMed
-
- Davis, J. Q., and Bennett, V. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269 27163-27166 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

