Loss of DNA ligase IV prevents recognition of DNA by double-strand break repair proteins XRCC4 and XLF
- PMID: 18782835
- PMCID: PMC2566893
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn552
Loss of DNA ligase IV prevents recognition of DNA by double-strand break repair proteins XRCC4 and XLF
Abstract
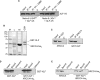
The repair of DNA double-strand breaks by nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) is essential for maintenance of genomic integrity and cell viability. Central to the molecular mechanism of NHEJ is DNA ligase IV/XRCC4/XLF complex, which rejoins the DNA. During adenovirus (Ad5) infection, ligase IV is targeted for degradation in a process that requires expression of the viral E1B 55k and E4 34k proteins while XRCC4 and XLF protein levels remain unchanged. We show that in Ad5-infected cells, loss of ligase IV is accompanied by loss of DNA binding by XRCC4. Expression of E1B 55k and E4 34k was sufficient to cause loss of ligase IV and loss of XRCC4 DNA binding. Using ligase IV mutant human cell lines, we determined that the absence of ligase IV, and not expression of viral proteins, coincided with inhibition of DNA binding by XRCC4. In ligase IV mutant human cell lines, DNA binding by XLF was also inhibited. Expression of both wild-type and adenylation-mutant ligase IV in ligase IV-deficient cells restored DNA binding by XRCC4. These data suggest that the intrinsic DNA-binding activities of XRCC4 and XLF may be subject to regulation and are down regulated in human cells that lack ligase IV.
Figures

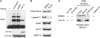



References
-
- Critchlow SE, Bowater RP, Jackson SP. Mammalian DNA double-strand break repair protein Xrcc4 interacts with DNA ligase IV. Curr. Biol. 1997;7:588–598. - PubMed
-
- Grawunder U, Wilm M, Wu XT, Kulesza P, Wilson TE, Mann M, Lieber MR. Activity of DNA ligase IV stimulated by complex formation with Xrcc4 protein in mammalian cells. Nature. 1997;388:492–495. - PubMed
-
- Grawunder U, Zimmer D, Kulesza P, Lieber MR. Requirement for an interaction of Xrcc4 with DNA ligase IV for wild-type V(D)J recombination and DNA double-strand break repair in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:24708–24714. - PubMed
-
- Modesti M, Junop MS, Ghirlando R, van de Rakt M, Gellert M, Yang W, Kanaar R. Tetramerization and DNA ligase IV interaction of the DNA double-strand break repair protein XRCC4 are mutually exclusive. J. Mol. Biol. 2003;334:215–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

