Influences of gender on the interaction between sympathetic nerve traffic and central adiposity
- PMID: 18782878
- PMCID: PMC5393368
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2007-2820
Influences of gender on the interaction between sympathetic nerve traffic and central adiposity
Abstract
Context: Sympathetic activation promotes insulin resistance and arterial hypertension with increasing adiposity. A difference in the relationship between adiposity and sympathetic activity between women and men could contribute to the known gender difference in cardiovascular disease risk.
Objective: We tested whether muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) is correlated differently with waist circumference, waist to hip ratio (WHR), and body mass index (BMI) in women and men.
Design and setting: We pooled data from two microneurography centers (Berlin, Germany; Gdansk, Poland) for a cross-sectional study.
Participants: We studied 111 normotensive, healthy Caucasian subjects (70 males and 41 females). Age ranged between 19 and 62 yr and BMI ranged between 18 and 40 kg/m(2).
Intervention: No intervention was applied during the study.
Measurements: Supine heart rate, blood pressure, and MSNA were recorded after at least 30 min rest.
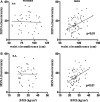
Results: MSNA in bursts per minute was age dependent in both sexes [r (male) = 0.56, r (female) = 0.34, P < 0.01]. Controlling for waist and hip circumferences, age dependence remained highly significant in men (r = 0.43) and women (r = 0.43). Adjusting for age, in men, waist circumference (r = 0.29), WHR (r = 0.39), and BMI (r = 0.31) were predictive for MSNA and directly correlated (P < 0.01) but not in women. Adjusting for BMI, in men, only WHR (r = 0.40) remained predictive for MSNA.
Conclusion: These data support the hypothesis of a gender difference in the regulation of the sympathetic nervous system, in which MSNA mainly relates to WHR in men but not women. The phenomenon may contribute to the sexual dimorphism in cardiovascular disease risk.
Figures
References
-
- Fagius J 2003. Sympathetic nerve activity in metabolic control—some basic concepts. Acta Physiol Scand 177:337–343 - PubMed
-
- Grassi G, Dell'Oro R, Facchini A, Quarti TF, Bolla GB, Mancia G 2004. Effect of central and peripheral body fat distribution on sympathetic and baroreflex function in obese normotensives. J Hypertens 22:2363–2369 - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro MM, Trombetta IC, Batalha LT, Rondon MU, Forjaz CL, Barretto AC, Villares SM, Negrao CE 2001. Muscle sympathetic nerve activity and hemodynamic alterations in middle-aged obese women. Braz J Med Biol Res 2001 34:475–478 - PubMed
-
- Narkiewicz K, van de Borne PJ, Cooley RL, Dyken ME, Somers VK 1998. Sympathetic activity in obese subjects with and without obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 98:772–776 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez GE, Beske SD, Ballard TP, Davy KP 2002. Sympathetic neural activation in visceral obesity. Circulation 106:2533–2536 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources