Effects of hypocretin (orexin) neuronal loss on sleep and extracellular adenosine levels in the rat basal forebrain
- PMID: 18783368
- PMCID: PMC2747316
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06424.x
Effects of hypocretin (orexin) neuronal loss on sleep and extracellular adenosine levels in the rat basal forebrain
Abstract
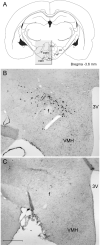
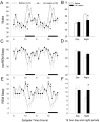
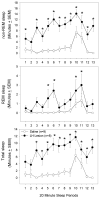
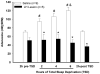
Neurons containing the neuropeptide hypocretin (HCRT, orexin) are localized only in the lateral hypothalamus, from where they innervate multiple regions implicated in arousal, including the basal forebrain. HCRT activation of downstream arousal neurons is likely to stimulate release of endogenous factors. One such factor is adenosine, which in the basal forebrain increases in level with wakefulness and decreases with sleep, and is hypothesized to regulate the waxing and waning of sleep drive. Does loss of HCRT neurons affect adenosine levels in the basal forebrain? Is the increased sleep that accompanies HCRT loss a consequence of higher adenosine levels in the basal forebrain? In the present study, we investigated these questions by lesioning the HCRT neurons with HCRT-2-saporin (HCRT-2-SAP) and measuring sleep and extracellular levels of adenosine in the basal forebrain. In separate groups of rats, the neurotoxin HCRT-2-SAP or saline was administered locally to the lateral hypothalamus, and 80 days later adenosine and sleep were assessed. Rats given the neurotoxin had a 94% loss of HCRT neurons. These rats woke less at night, and had more rapid eye movement sleep, which is consistent with HCRT hypofunction. These rats also had more sleep after brief periods of sleep deprivation. However, in the lesioned rats, adenosine levels did not increase with 6 h of sleep deprivation, whereas an increase in adenosine levels occurred in rats without lesion of the HCRT neurons. These findings indicate that adenosine levels do not increase with wakefulness in rats with a HCRT lesion, and that the increased sleep in these rats occurs independently of adenosine levels in the basal forebrain.
Similar articles
-
Hypocretin/orexin antagonism enhances sleep-related adenosine and GABA neurotransmission in rat basal forebrain.Brain Struct Funct. 2016 Mar;221(2):923-40. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0946-y. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Brain Struct Funct. 2016. PMID: 25431268
-
Hypocretin-2 saporin lesions of the ventrolateral periaquaductal gray (vlPAG) increase REM sleep in hypocretin knockout mice.PLoS One. 2009 Jul 22;4(7):e6346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006346. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19623260 Free PMC article.
-
Hypocretin-2-saporin lesions of the lateral hypothalamus produce narcoleptic-like sleep behavior in the rat.J Neurosci. 2001 Sep 15;21(18):7273-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07273.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11549737 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin/hypocretin modulation of the basal forebrain cholinergic system: insights from in vivo microdialysis studies.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008 Aug;90(2):156-62. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.01.008. Epub 2008 Jan 19. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008. PMID: 18281084 Review.
-
Activation of the basal forebrain by the orexin/hypocretin neurones.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2010 Mar;198(3):223-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2009.02036.x. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2010. PMID: 19723027 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saporin from Saponaria officinalis as a Tool for Experimental Research, Modeling, and Therapy in Neuroscience.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Aug 25;12(9):546. doi: 10.3390/toxins12090546. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32854372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric Interactions between Adenosine A2A and Dopamine D2 Receptors in Heteromeric Complexes: Biochemical and Pharmacological Characteristics, and Opportunities for PET Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 9;22(4):1719. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041719. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential role of the orexin system in premenstrual syndrome.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 16;14:1266806. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1266806. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38292774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optogenetic deconstruction of sleep-wake circuitry in the brain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2010 Jan 20;2:31. doi: 10.3389/neuro.02.031.2009. eCollection 2010. Front Mol Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20126433 Free PMC article.
-
Intracerebral microdialysis of adenosine and adenosine monophosphate - a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of baseline concentrations.J Neurochem. 2018 Oct;147(1):58-70. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14552. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Neurochem. 2018. PMID: 30025168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassant MH, Apartis E, Jazat-Poindessous FR, Wiley RG, Lamour YA. Selective immunolesion of the basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: effects on hippocampal activity during sleep and wakefulness in the rat. Neurodegeneration. 1995;4:61–70. - PubMed
-
- Blanco-Centurion C, Shiromani A, Winston E, Shiromani PJ. Effects of hypocretin-1 in 192-IgG-saporin-lesioned rats. Eur.J.Neurosci. 2006a;24:2084–2088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous