IL-12 p80-dependent macrophage recruitment primes the host for increased survival following a lethal respiratory viral infection
- PMID: 18783467
- PMCID: PMC2673362
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02923.x
IL-12 p80-dependent macrophage recruitment primes the host for increased survival following a lethal respiratory viral infection
Abstract
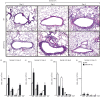
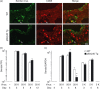
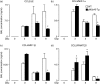
A protective immune response to a respiratory viral infection requires a series of coordinated cellular and molecular responses. We have previously demonstrated that increased expression of airway epithelial cell interleukin (IL)-12 p80, a macrophage chemoattractant, is associated with human respiratory viral infection and mediates post-viral mortality in the mouse. To better understand the role of IL-12 p80-dependent macrophage chemotaxis in mediating viral immunity, we generated a transgenic mouse strain utilizing a promoter to drive IL-12 p40 gene expression in the airway epithelium. This transgenic strain secreted biologically active IL-12 p80 in a lung-specific manner, and demonstrated a selective increase in the number of resident, unactivated airway macrophages at baseline. Following infection with a sublethal dose of mouse parainfluenza virus type 1 (Sendai virus), the transgenic mice demonstrated an earlier peak and decline in the number of airway inflammatory cells. The transgenic mice were resistant to a lethal dose of virus and this viral resistance was dependent on the increased number of airway macrophages at baseline as partial depletion prior to infection abrogated this phenotype. The survival advantage in the transgenic mice was independent of viral load but was associated with a more rapid decline in the number of airway inflammatory cells and concentrations of multiple chemokines including the CC chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2)/JE, CCL3/macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha, CCL4/MIP-1beta, and CCL5/RANTES. Collectively, these results suggest that IL-12 p80-driven increases in the number of resident airway macrophages prime the host for a protective immune response that can confer increased survival following a lethal respiratory viral infection.
Figures
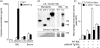
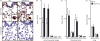
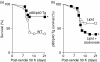

Similar articles
-
IL-12 p40 homodimer-dependent macrophage chemotaxis and respiratory viral inflammation are mediated through IL-12 receptor beta 1.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 15;171(12):6866-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.12.6866. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14662893
-
TREM-2 promotes macrophage survival and lung disease after respiratory viral infection.J Exp Med. 2015 May 4;212(5):681-97. doi: 10.1084/jem.20141732. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25897174 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-nonspecific recruitment of Th2 cells to the lung as a mechanism for viral infection-induced allergic asthma.J Immunol. 2002 Nov 15;169(10):5458-67. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.5458. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12421921
-
Chemokines in viral disease.Res Virol. 1996 Mar-Jun;147(2-3):131-8. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(96)80227-5. Res Virol. 1996. PMID: 8901432 Review.
-
Host epithelial-viral interactions as cause and cure for asthma.Curr Opin Immunol. 2011 Aug;23(4):487-94. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.05.010. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21703838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of hydrogel nanoparticle size and functionalization on in vivo behavior for lung imaging and therapeutics.Mol Pharm. 2009 Nov-Dec;6(6):1891-902. doi: 10.1021/mp900215p. Mol Pharm. 2009. PMID: 19852512 Free PMC article.
-
Increased production of IL-4 and IL-12p40 from bronchoalveolar lavage cells are biomarkers of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the sputum.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059461. Epub 2013 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527200 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar macrophages contribute to the pathogenesis of human metapneumovirus infection while protecting against respiratory syncytial virus infection.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014 Oct;51(4):502-15. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0414OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24749674 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, and in vivo efficacy of shell cross-linked nanoparticle formulations carrying silver antimicrobials as aerosolized therapeutics.ACS Nano. 2013 Jun 25;7(6):4977-87. doi: 10.1021/nn400322f. Epub 2013 Jun 4. ACS Nano. 2013. PMID: 23718195 Free PMC article.
-
Azithromycin attenuates airway inflammation in a mouse model of viral bronchiolitis.Respir Res. 2010 Jun 30;11(1):90. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-90. Respir Res. 2010. PMID: 20591166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Russell TD, Yan Q, Fan G, Khalifah AP, Bishop DK, Brody SL, Walter MJ. IL-12 p40 homodimer-dependent macrophage chemotaxis and respiratory viral inflammation are mediated through IL-12 receptor beta1. J Immunol. 2003;171:6866–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

