Development of an O(6)-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase assay based on covalent transfer of the benzyl moiety from [benzene-3H]O(6)-benzylguanine to the protein
- PMID: 18783719
- PMCID: PMC2773450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2008.08.009
Development of an O(6)-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase assay based on covalent transfer of the benzyl moiety from [benzene-3H]O(6)-benzylguanine to the protein
Abstract
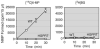
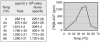
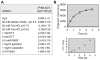
Although it is known that (i) O(6)-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AGT) confers tumor cell resistance to guanine O(6)-targeting drugs such as cloretazine, carmustine, and temozolomide and that (ii) AGT levels in tumors are highly variable, measurement of AGT activity in tumors before treatment is not a routine clinical practice. This derives in part from the lack of a reliable clinical AGT assay; therefore, a simple AGT assay was devised based on transfer of radioactive benzyl residues from [benzene-3H]O(6)-benzylguanine ([3H]BG) to AGT. The assay involves incubation of intact cells or cell homogenates with [3H]BG and measurement of radioactivity in a 70% methanol precipitable fraction. Approximately 85% of AGT in intact cells was recovered in cell homogenates. Accuracy of the AGT assay was confirmed by examination of AGT levels by Western blot analysis with the exception of false-positive results in melanin-containing cells due to [3H]BG binding to melanin. Second-order kinetic constants for human and murine AGT were 1100 and 380 M(-1)s(-1), respectively. AGT levels in various human cell lines ranged from less than 500 molecules/cell (detection limit) to 45,000 molecules/cell. Rodent cell lines frequently lacked AGT expression, and AGT levels in rodent cells were much lower than in human cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Measurement of O(6)-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase activity in tumour cells using stable isotope dilution HPLC-ESI-MS/MS.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 Oct 15;1033-1034:138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.08.010. Epub 2016 Aug 8. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27544051
-
Inactivation of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase by 8-substituted O6-benzylguanine analogs in mice.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001;47(1):63-9. doi: 10.1007/s002800000202. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11221964
-
Heterogeneity of O6-alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase measured by flow cytometric analysis in blood and bone marrow mononuclear cells.Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Feb;4(2):475-81. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9516939
-
Conserved residue lysine165 is essential for the ability of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase to react with O6-benzylguanine.Biochem J. 2000 Apr 15;347(Pt 2):527-34. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3470527. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10749683 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of MGMT in the treatment of cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2002 May 1;20(9):2388-99. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.06.110. J Clin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 11981013 Review.
Cited by
-
pH-dependent general base catalyzed activation rather than isocyanate liberation may explain the superior anticancer efficacy of laromustine compared to related 1,2-bis(methylsulfonyl)-1-(2-chloroethyl)hydrazine prodrugs.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018 Jan;91(1):62-74. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13057. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018. PMID: 28636806 Free PMC article.
-
Reductive activation of the prodrug 1,2-bis(methylsulfonyl)-1-(2-chloroethyl)-2-[[1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethoxy]carbonyl]hydrazine (KS119) selectively occurs in oxygen-deficient cells and overcomes O(6)-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase mediated KS119 tumor cell resistance.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 1;79(11):1553-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.12.004. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20005211 Free PMC article.
-
MGMT promoter methylation in triple negative breast cancer of the GeparSixto trial.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 25;15(8):e0238021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238021. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32841306 Free PMC article.
-
Every OGT Is Illuminated … by Fluorescent and Synchrotron Lights.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 5;18(12):2613. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122613. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29206193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design Strategy for the EPR Tumor-Targeting of 1,2-Bis(sulfonyl)-1-alkylhydrazines.Molecules. 2021 Jan 6;26(2):259. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020259. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33419160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shyam K, Penketh PG, Loomis RH, Rose WC, Sartorelli AC. Antitumor 2-(aminocarbonyl)-1,2-bis(methylsulfonyl)-1-(2-chloroethyl)hydrazines. J. Med. Chem. 1996;39:796–801. - PubMed
-
- Ludlum DB. The chloroethylnitrosoureas: sensitivity and resistance to cancer chemotherapy at the molecular level. Cancer Invest. 1997;15:588–598. - PubMed
-
- Newlands ES, Stevens MF, Wedge SR, Wheelhouse RT, Brock C. Temozolomide:a review of its discovery, chemical properties, pre-clinical development, and clinical trials. Cancer Treat. Rev. 1997;23:35–61. - PubMed
-
- Ludlum DB. DNA alkylation by the haloethylnitrosoureas: nature of modifications produced and their enzymatic repair or removal. Mutat. Res. 1990;233:117–126. - PubMed
-
- Penketh PG, Shyam K, Sartorelli AC. Comparison of DNA lesions produced by tumor-inhibitory 1,2-bis(sulfonyl)hydrazines and chloroethylnitrosoureas. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000;59:283–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

