Crystal structure of metastasis-associated protein S100A4 in the active calcium-bound form
- PMID: 18783790
- PMCID: PMC2644285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.076
Crystal structure of metastasis-associated protein S100A4 in the active calcium-bound form
Abstract
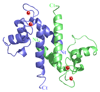
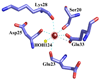
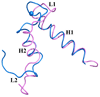
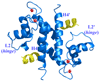
S100A4 (metastasin) is a member of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins that is directly involved in tumorigenesis. Until recently, the only structural information available was the solution NMR structure of the inactive calcium-free form of the protein. Here we report the crystal structure of human S100A4 in the active calcium-bound state at 2.03 A resolution that was solved by molecular replacement in the space group P6(5) with two molecules in the asymmetric unit from perfectly merohedrally twinned crystals. The Ca(2+)-bound S100A4 structure reveals a large conformational change in the three-dimensional structure of the dimeric S100A4 protein upon calcium binding. This calcium-dependent conformational change opens up a hydrophobic binding pocket that is capable of binding to target proteins such as annexin A2, the tumor-suppressor protein p53 and myosin IIA. The structure of the active form of S100A4 provides insight into its interactions with its binding partners and a better understanding of its role in metastasis.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Structure of Ca2+-bound S100A4 and its interaction with peptides derived from nonmuscle myosin-IIA.Biochemistry. 2008 May 6;47(18):5111-26. doi: 10.1021/bi702537s. Epub 2008 Apr 15. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18410126 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the metastasis-associated protein, S100A4. Roles of calcium binding and dimerization in cellular localization and interaction with myosin.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 8;278(32):30063-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304909200. Epub 2003 May 19. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12756252
-
Phenothiazines inhibit S100A4 function by inducing protein oligomerization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 11;107(19):8605-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0913660107. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20421509 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis-associated protein S100A4: spotlight on its role in cell migration.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007 May;7(3):217-28. doi: 10.2174/156800907780618329. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17504119 Review.
-
S100A4 calcium-binding protein is key player in tumor progression and metastasis: preclinical and clinical evidence.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012 Jun;31(1-2):163-72. doi: 10.1007/s10555-011-9338-4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012. PMID: 22109080 Review.
Cited by
-
The solution structure of human calcium-bound S100A4 mutated at four cysteine loci.J Biomol NMR. 2015 Jun;62(2):233-8. doi: 10.1007/s10858-015-9927-6. Epub 2015 Apr 9. J Biomol NMR. 2015. PMID: 25855140 No abstract available.
-
Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship exploration of 1-substituted 4-aroyl-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-2(5H)-one analogues as inhibitors of the annexin A2-S100A10 protein interaction.J Med Chem. 2011 Apr 14;54(7):2080-94. doi: 10.1021/jm101212e. Epub 2011 Mar 4. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21375334 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-S100A4 antibody suppresses metastasis formation by blocking stroma cell invasion.Neoplasia. 2012 Dec;14(12):1260-8. doi: 10.1593/neo.121554. Neoplasia. 2012. PMID: 23308057 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of S100A4 in the mouse lens induces an aberrant retina-specific differentiation program and cataract.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 26;11(1):2203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81611-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33500475 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the Ca²+-dependent interaction between S100A4 and tail fragments of nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA.J Mol Biol. 2011 Jan 28;405(4):1004-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.11.036. Epub 2010 Nov 24. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21110983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schafer BW, Heizmann CW. The S100 family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: functions and pathology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996;21:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Zimmer DB, Cornwall EH, Landar A, Song W. The S100 protein family: history, function, and expression. Brain Res. Bull. 1995;37:417–429. - PubMed
-
- Heizmann CW, Fritz G, Schafer BW. S100 proteins: structure, functions and pathology. Front Biosci. 2002;7:1356–1368. - PubMed
-
- Marenholz I, Heizmann CW, Fritz G. S100 proteins in mouse and man: from evolution to function and pathology (including an update of the nomenclature) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004;322:1111–1122. - PubMed
-
- Donato R. S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2001;33:637–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

