Crystal structure of metastasis-associated protein S100A4 in the active calcium-bound form
- PMID: 18783790
- PMCID: PMC2644285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.076
Crystal structure of metastasis-associated protein S100A4 in the active calcium-bound form
Abstract
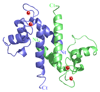
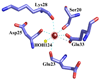
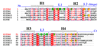
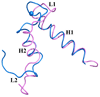
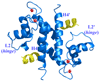
S100A4 (metastasin) is a member of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins that is directly involved in tumorigenesis. Until recently, the only structural information available was the solution NMR structure of the inactive calcium-free form of the protein. Here we report the crystal structure of human S100A4 in the active calcium-bound state at 2.03 A resolution that was solved by molecular replacement in the space group P6(5) with two molecules in the asymmetric unit from perfectly merohedrally twinned crystals. The Ca(2+)-bound S100A4 structure reveals a large conformational change in the three-dimensional structure of the dimeric S100A4 protein upon calcium binding. This calcium-dependent conformational change opens up a hydrophobic binding pocket that is capable of binding to target proteins such as annexin A2, the tumor-suppressor protein p53 and myosin IIA. The structure of the active form of S100A4 provides insight into its interactions with its binding partners and a better understanding of its role in metastasis.
Figures












References
-
- Schafer BW, Heizmann CW. The S100 family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: functions and pathology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996;21:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Zimmer DB, Cornwall EH, Landar A, Song W. The S100 protein family: history, function, and expression. Brain Res. Bull. 1995;37:417–429. - PubMed
-
- Heizmann CW, Fritz G, Schafer BW. S100 proteins: structure, functions and pathology. Front Biosci. 2002;7:1356–1368. - PubMed
-
- Marenholz I, Heizmann CW, Fritz G. S100 proteins in mouse and man: from evolution to function and pathology (including an update of the nomenclature) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004;322:1111–1122. - PubMed
-
- Donato R. S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2001;33:637–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

