The thrombin-sensitive region of protein S mediates phospholipid-dependent interaction with factor Xa
- PMID: 18784085
- PMCID: PMC2586267
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806527200
The thrombin-sensitive region of protein S mediates phospholipid-dependent interaction with factor Xa
Abstract
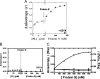
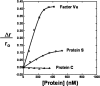
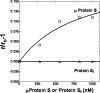
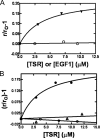
To test the hypothesis that factor Xa (fXa) interacts with protein S, fXa was labeled active-site specifically with a dansyl (D) dye via a Glu-Gly-Arg (EGR) tether to yield DEGR-fXa(i). When protein S was added to phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylserine (PC/PS, 4:1) vesicle-bound DEGR-fXa(i), the anisotropy of the dansyl moiety was altered from 0.219 +/- 0.002 to 0.245 +/- 0.003. This change in dansyl anisotropy was not observed when DEGR-Xa(i) was titrated with protein S in the absence of PC/PS vesicles, or in the presence of 100% PC vesicles, or when PC/PS vesicle-bound DEGR-fXa(i) was titrated with thrombin-cleaved protein S. The protein S-dependent dansyl fluorescence change was specific for fXa because it was not observed for two homologous and similarly labeled DEGR-fIXa(i) and DEGR-fVIIa(i). Furthermore, protein S specifically and saturably altered the fluorescence anisotropy of PC/PS-bound active site-labeled LWB-FPR-fXa(i) (Kd = 33 nm) and was photocross-linked to PC/PS-bound LWB-FPR-fXa(i) analog, independently confirming the above results. Chemically synthesized microprotein S, comprising residues 1-116 of protein S and including the gamma-carboxyglutamic-rich domain, the thrombin-sensitive region (TSR), and the first epidermal growth factor-like domain (EGF1) of protein S, altered the anisotropy of PC/PS-bound DEGR-fXa(i) from 0.219 to 0.242, similar to the effect of the protein S titration (Kd = 303 nm), suggesting that microprotein S binds to DEGR-fXa(i). To identify individual protein S domain(s) that binds DEGR-fXa(i), the EGF1 and TSR domains were chemically synthesized and studied. The TSR altered the anisotropy of DEGR-fXa(i) by approximately 16% (Kd = 3.9 microm), but the EGF1 domain had no effect on the signal. In controls, the TSR domain did not alter the anisotropy of DEGR-fIXa(i) and DEGR-fVIIa(i), respectively. These data demonstrate that membrane-bound fXa binding to protein S involves the TSR of protein S.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Implication of protein S thrombin-sensitive region with membrane binding via conformational changes in the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-rich domain.Biochem J. 2001 Dec 1;360(Pt 2):499-506. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3600499. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11716779 Free PMC article.
-
The active site of factor IXa is located far above the membrane surface and its conformation is altered upon association with factor VIIIa. A fluorescence study.J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17012-21. J Biol Chem. 1992. PMID: 1512240
-
Factor XA binding to phosphatidylserine-containing membranes produces an inactive membrane-bound dimer.Biophys J. 2009 Oct 21;97(8):2232-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.07.043. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19843455 Free PMC article.
-
Glucosylceramide, a neutral glycosphingolipid anticoagulant cofactor, enhances the interaction of human- and bovine-activated protein C with negatively charged phospholipid vesicles.J Biol Chem. 2003 Apr 25;278(17):14614-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206746200. Epub 2003 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12560338
-
Phosphatidylserine and FVa regulate FXa structure.Biochem J. 2014 Apr 1;459(1):229-39. doi: 10.1042/BJ20131099. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 24467409 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Plasma protein S contains zinc essential for efficient activated protein C-independent anticoagulant activity and binding to factor Xa, but not for efficient binding to tissue factor pathway inhibitor.FASEB J. 2009 Jul;23(7):2244-53. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-123174. Epub 2009 Feb 24. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19244162 Free PMC article.
-
Bisaryl hydrazones as exchangeable biocompatible linkers.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010 Mar 8;49(11):2023-7. doi: 10.1002/anie.200906756. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010. PMID: 20183838 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Plasma protein S residues 37-50 mediate its binding to factor Va and inhibition of blood coagulation.Thromb Haemost. 2013 Aug;110(2):275-82. doi: 10.1160/TH12-12-0953. Epub 2013 May 23. Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23892573 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: structure-function.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jan 1;17(1):262-80. doi: 10.2741/3926. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Kunitz-3 domain of TFPI-alpha is required for protein S-dependent enhancement of factor Xa inhibition.Blood. 2010 Aug 26;116(8):1344-51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-10-246686. Epub 2010 May 17. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20479289 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

