Regulation of synaptic efficacy in hypocretin/orexin-containing neurons by melanin concentrating hormone in the lateral hypothalamus
- PMID: 18784290
- PMCID: PMC2562258
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1766-08.2008
Regulation of synaptic efficacy in hypocretin/orexin-containing neurons by melanin concentrating hormone in the lateral hypothalamus
Abstract
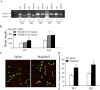
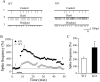
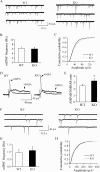
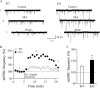
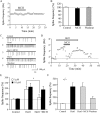
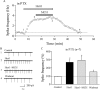
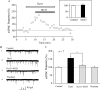
The lateral hypothalamus (LH) is a central hub that integrates inputs from, and sends outputs to, many other brain areas. Two groups of neurons in the LH, expressing hypocretin/orexin or melanin concentrating hormone (MCH), have been shown to participate in sleep regulation, energy homeostasis, drug addiction, motor regulation, stress response, and social behaviors. The elucidation of crosstalk between these two systems is essential to understand these behaviors and functions because there is evidence that there are reciprocal innervations between hypocretin/orexin and MCH neurons. In this study, we used MCH receptor-1 knock-out (MCHR1 KO) and wild-type (WT) mice expressing green fluorescent protein in hypocretin/orexin-containing neurons to examine the hypothesis that MCH modulates hypocretin/orexin-mediated effects on behavioral state and synaptic transmission in the LH. In MCHR1 KO mice, the efficacy of glutamatergic synapses on hypocretin/orexin neurons is potentiated and hypocretin-1-induced action potential firing is facilitated, potentially explaining an increased effect of modafinil observed in MCHR1 KO mice. In wild-type mice with intact MCHR1 signaling, MCH significantly attenuated the hypocretin-1-induced enhancement of spike frequency in hypocretin/orexin neurons. The MCH effect was dose dependent, pertussis toxin sensitive, and was abolished in MCHR1 KO mice. Consistent with this effect, MCH attenuated hypocretin-1-induced enhancement of the frequency of miniature EPSCs in hypocretin/orexin neurons. These data from MCHR1 KO and WT mice demonstrate a novel interaction between these two systems, implying that MCH may exert a unique inhibitory influence on hypocretin/orexin signaling as a way to fine-tune the output of the LH.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrophysiological effects of MCH on neurons in the hypothalamus.Peptides. 2009 Nov;30(11):2025-30. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.05.006. Epub 2009 May 20. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19463877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanin concentrating hormone depresses synaptic activity of glutamate and GABA neurons from rat lateral hypothalamus.J Physiol. 2001 May 15;533(Pt 1):237-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0237b.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11351031 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic evidence for inhibitory signaling from orexin to MCH neurons via local microcircuits.J Neurosci. 2015 Apr 8;35(14):5435-41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5269-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25855162 Free PMC article.
-
Neurochemical Heterogeneity Among Lateral Hypothalamic Hypocretin/Orexin and Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Neurons Identified Through Single-Cell Gene Expression Analysis.eNeuro. 2017 Sep 22;4(5):ENEURO.0013-17.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0013-17.2017. eCollection 2017 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 28966976 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral hypothalamus as a sensor-regulator in respiratory and metabolic control.Physiol Behav. 2013 Sep 10;121:117-24. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.03.023. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Physiol Behav. 2013. PMID: 23562864 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The anatomical, cellular and synaptic basis of motor atonia during rapid eye movement sleep.J Physiol. 2016 Oct 1;594(19):5391-414. doi: 10.1113/JP271324. Epub 2016 Jul 3. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27060683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Voluntary Sleep Loss in Rats.Sleep. 2016 Jul 1;39(7):1467-79. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5984. Sleep. 2016. PMID: 27166236 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of hypocretin attenuates extended access of cocaine self-administration in rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Nov;43(12):2373-2382. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0054-4. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29703996 Free PMC article.
-
The hypocretins (orexins) mediate the "phasic" components of REM sleep: A new hypothesis.Sleep Sci. 2014 Mar;7(1):19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.slsci.2014.07.021. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Sleep Sci. 2014. PMID: 26483897 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological effects of MCH on neurons in the hypothalamus.Peptides. 2009 Nov;30(11):2025-30. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.05.006. Epub 2009 May 20. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19463877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahnaou A, Drinkenburg WH, Bouwknecht JA, Alcazar J, Steckler T, Dautzenberg FM. Blocking melanin-concentrating hormone MCH(1) receptor affects rat sleep-wake architecture. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;579:177–188. - PubMed
-
- Bächner D, Kreienkamp H, Weise C, Buck F, Richter D. Identification of melanin concentrating hormone (MCH) as the natural ligand for the orphan somatostatin-like receptor 1 (SLC-1) FEBS Lett. 1999;457:522–524. - PubMed
-
- Bayer L, Eggermann E, Serafin M, Grivel J, Machard D, Muhlethaler M, Jones BE. Opposite effects of noradrenaline and acetylcholine upon hypocretin/orexin versus melanin concentrating hormone neurons in rat hypothalamic slices. Neuroscience. 2005;130:807–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
