Adaptation of velocity encoding in synaptically coupled neurons in the fly visual system
- PMID: 18784299
- PMCID: PMC6670915
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1936-08.2008
Adaptation of velocity encoding in synaptically coupled neurons in the fly visual system
Abstract
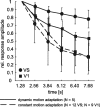
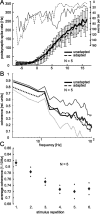
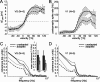
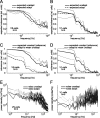
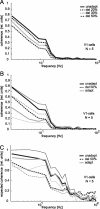
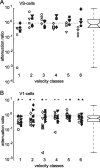
Although many adaptation-induced effects on neuronal response properties have been described, it is often unknown at what processing stages in the nervous system they are generated. We focused on fly visual motion-sensitive neurons to identify changes in response characteristics during prolonged visual motion stimulation. By simultaneous recordings of synaptically coupled neurons, we were able to directly compare adaptation-induced effects at two consecutive processing stages in the fly visual motion pathway. This allowed us to narrow the potential sites of adaptation effects within the visual system and to relate them to the properties of signal transfer between neurons. Motion adaptation was accompanied by a response reduction, which was somewhat stronger in postsynaptic than in presynaptic cells. We found that the linear representation of motion velocity degrades during adaptation to a white-noise velocity-modulated stimulus. This effect is caused by an increasingly nonlinear velocity representation rather than by an increase of noise and is similarly strong in presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons. In accordance with this similarity, the dynamics and the reliability of interneuronal signal transfer remained nearly constant. Thus, adaptation is mainly based on processes located in the presynaptic neuron or in more peripheral processing stages. In contrast, changes of transfer properties at the analyzed synapse or in postsynaptic spike generation contribute little to changes in velocity coding during motion adaptation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synaptic transfer of dynamic motion information between identified neurons in the visual system of the blowfly.Neuroscience. 2003;119(4):1103-12. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(03)00204-5. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 12831867
-
Robust integration of motion information in the fly visual system revealed by single cell photoablation.J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 26;26(30):7898-906. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1327-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16870735 Free PMC article.
-
Motion adaptation leads to parsimonious encoding of natural optic flow by blowfly motion vision system.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Sep;94(3):1761-9. doi: 10.1152/jn.00308.2005. Epub 2005 May 25. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15917319
-
Neural encoding of behaviourally relevant visual-motion information in the fly.Trends Neurosci. 2002 Feb;25(2):96-102. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(02)02063-5. Trends Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11814562 Review.
-
Velocity computation in the primate visual system.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008 Sep;9(9):686-95. doi: 10.1038/nrn2472. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19143050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptation accentuates responses of fly motion-sensitive visual neurons to sudden stimulus changes.Proc Biol Sci. 2009 Oct 22;276(1673):3711-9. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.0596. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Proc Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19656791 Free PMC article.
-
The many facets of adaptation in fly visual motion processing.Commun Integr Biol. 2009;2(1):17-9. doi: 10.4161/cib.2.1.7350. Commun Integr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19704857 Free PMC article.
-
Disentangling of Local and Wide-Field Motion Adaptation.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Aug 31;15:713285. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.713285. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 34531728 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulation of insect motion vision.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2020 Mar;206(2):125-137. doi: 10.1007/s00359-019-01383-9. Epub 2019 Dec 6. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31811398 Review.
-
Spatio-temporal dynamics of impulse responses to figure motion in optic flow neurons.PLoS One. 2015 May 8;10(5):e0126265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126265. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25955416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckers U, Egelhaaf M, Kurtz R. Synapses in the fly motion-vision pathway: evidence for a broad range of signal amplitudes and dynamics. J Neurophysiol. 2007;97:2032–2041. - PubMed
-
- Borst A, Egelhaaf M. Temporal modulation of luminance adapts time constant of fly movement detectors. Biol Cybern. 1987;56:209–215.
-
- Borst A, Haag J. Effects of mean firing on neural information rate. J Comput Neurosci. 2001;10:213–221. - PubMed
-
- Borst A, Reisenman C, Haag J. Adapation of response transients in fly motion vision. II. Model studies. Vision Res. 2003;43:1311–1324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
