LIS1 and NDEL1 coordinate the plus-end-directed transport of cytoplasmic dynein
- PMID: 18784752
- PMCID: PMC2567412
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.182
LIS1 and NDEL1 coordinate the plus-end-directed transport of cytoplasmic dynein
Abstract
LIS1 was first identified as a gene mutated in human classical lissencephaly sequence. LIS1 is required for dynein activity, but the underlying mechanism is poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that LIS1 suppresses the motility of cytoplasmic dynein on microtubules (MTs), whereas NDEL1 releases the blocking effect of LIS1 on cytoplasmic dynein. We demonstrate that LIS1, cytoplasmic dynein and MT fragments co-migrate anterogradely. When LIS1 function was suppressed by a blocking antibody, anterograde movement of cytoplasmic dynein was severely impaired. Immunoprecipitation assay indicated that cytoplasmic dynein forms a complex with LIS1, tubulins and kinesin-1. In contrast, immunoabsorption of LIS1 resulted in disappearance of co-precipitated tubulins and kinesin. Thus, we propose a novel model of the regulation of cytoplasmic dynein by LIS1, in which LIS1 mediates anterograde transport of cytoplasmic dynein to the plus end of cytoskeletal MTs as a dynein-LIS1 complex on transportable MTs, which is a possibility supported by our data.
Figures
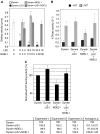
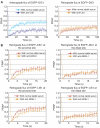
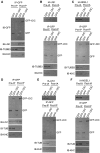
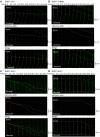

References
-
- Bingham JB, King SJ, Schroer TA (1998) Purification of dynactin and dynein from brain tissue. Methods Enzymol 298: 171–184 - PubMed
-
- Dobyns WB, Reiner O, Carrozzo R, Ledbetter DH (1993) Lissencephaly. A human brain malformation associated with deletion of the LIS1 gene located at chromosome 17p13. JAMA 270: 2838–2842 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

