Function and dysfunction of the PI system in membrane trafficking
- PMID: 18784754
- PMCID: PMC2536629
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.169
Function and dysfunction of the PI system in membrane trafficking
Abstract
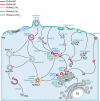
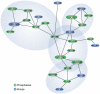
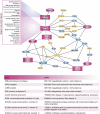
The phosphoinositides (PIs) function as efficient and finely tuned switches that control the assembly-disassembly cycles of complex molecular machineries with key roles in membrane trafficking. This important role of the PIs is mainly due to their versatile nature, which is in turn determined by their fast metabolic interconversions. PIs can be tightly regulated both spatially and temporally through the many PI kinases (PIKs) and phosphatases that are distributed throughout the different intracellular compartments. In spite of the enormous progress made in the past 20 years towards the definition of the molecular details of PI-protein interactions and of the regulatory mechanisms of the individual PIKs and phosphatases, important issues concerning the general principles of the organisation of the PI system and the coordination of the different PI-metabolising enzymes remain to be addressed. The answers should come from applying a systems biology approach to the study of the PI system, through the integration of analyses of the protein interaction data of the PI enzymes and the PI targets with those of the 'phenomes' of the genetic diseases that involve these PI-metabolising enzymes.
Figures
References
-
- Aoyagi K, Sugaya T, Umeda M, Yamamoto S, Terakawa S, Takahashi M (2005) The activation of exocytotic sites by the formation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate microdomains at syntaxin clusters. J Biol Chem 280: 17346–17352 - PubMed
-
- Attree O, Olivos IM, Okabe I, Bailey LC, Nelson DL, Lewis RA, McInnes RR, Nussbaum RL (1992) The Lowe's oculocerebrorenal syndrome gene encodes a protein highly homologous to inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase. Nature 358: 239–242 - PubMed
-
- Bai J, Chapman ER (2003) Application of fluorescent probes to study mechanics and dynamics of Ca2+-triggered synaptotagmin C2 domain–membrane interactions. Methods Enzymol 360: 238–258 - PubMed
-
- Behnia R, Munro S (2005) Organelle identity and the signposts for membrane traffic. Nature 438: 597–604 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

