Nodular lymphocyte-predominant hodgkin lymphoma or T-cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma: the problem in "grey zone" lymphomas
- PMID: 18784812
- PMCID: PMC2480562
Nodular lymphocyte-predominant hodgkin lymphoma or T-cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma: the problem in "grey zone" lymphomas
Abstract
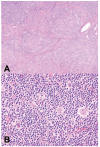
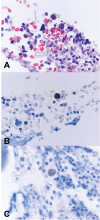
Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL) is a rare indolent B-cell lymphoma. However, its morphology can resemble T-cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma (T/HRBCL), a subtype of more aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. More and more studies suggest that these two entities are closely related. In this report, a 59-year-old man with nodal NLPHL and concomitant T/HRBCL in the bone marrow is presented, the current progress in our understanding of these two closely related B-cell lymphomas reviewed and the problems in the diagnosis and differentiation of NLPHL and T/HRBCL discussed.
Keywords: Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma; T-cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma; “grey zone” lymphoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma with nodules resembling T-cell/histiocyte-rich B-cell lymphoma: differential diagnosis between nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma and T-cell/histiocyte-rich B-cell lymphoma.Blood. 2003 Nov 15;102(10):3753-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-02-0626. Epub 2003 Jul 24. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12881319
-
Rituximab plus Ifosfamide, Carboplatin and Etoposide for T-Cell/Histiocyte-Rich B-Cell Lymphoma Arising in Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin's Lymphoma.Case Rep Oncol. 2012 May;5(2):413-9. doi: 10.1159/000341562. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Case Rep Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22949903 Free PMC article.
-
PD-1, a follicular T-cell marker useful for recognizing nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma.Am J Surg Pathol. 2008 Aug;32(8):1252-7. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318165b0d6. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18594468
-
Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Nodular Lymphocyte Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma: Variant Patterns, Borderlines and Mimics.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 16;13(12):3021. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123021. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34208705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: pathology, clinical course and relation to T-cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma.Pathology. 2020 Jan;52(1):142-153. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2019.10.003. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Pathology. 2020. PMID: 31785822 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific Polo-Like Kinase 1 Expression in Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma Suggests an Intact Immune Surveillance Program.Am J Pathol. 2024 Jan;194(1):165-178. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Am J Pathol. 2024. PMID: 37923249 Free PMC article.
-
Pitfalls in diagnostic hematopathology -- Part II.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2009 Sep 10;3(1):39-46. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19918327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Second malignancies in Hodgkin's disease: A review of the literature and report of a case with a secondary Lennert's lymphoma.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2014 Sep;18(Suppl 1):S90-5. doi: 10.4103/0973-029X.141332. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25364188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Case of Chemotherapy-Refractory "THRLBCL like Transformation of NLPHL" Successfully Treated with Lenalidomide.Case Rep Oncol Med. 2018 Feb 6;2018:6137454. doi: 10.1155/2018/6137454. eCollection 2018. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2018. PMID: 29552367 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Pathobiology of Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Potential Impact on Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Strategies.Adv Hematol. 2011;2011:439456. doi: 10.1155/2011/439456. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Adv Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21318045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mason DY, Banks PM, Chan J, Cleary ML, Delsol G, de Wolf Peeters C, Falini B, Gatter K, Grogan TM, Harris NL, et al. Nodular lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin's disease. A distinct clinicopathological entity. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994;18:526–530. - PubMed
-
- Marafioti T, Hummel M, Anagnostopoulos I, Foss HD, Falini B, Delsol G, Isaacson PG, Pileri S, Stein H. Origin of nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's disease from a clonal expansion of highly mutated germinal-center B cells. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:453–458. - PubMed
-
- Ohno T, Stribley JA, Wu G, Hinrichs SH, Weisenburger DD, Chan WC. Clonality in nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:459–465. - PubMed
-
- Wlodarska I, Nooyen P, Maes B, Martin-Subero JI, Siebert R, Pauwels P, De Wolf-Peeters C, Hagemeijer A. Frequent occurrence of BCL6 rearrangements in nodular lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin lymphoma but not in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2003;101:706–710. - PubMed
-
- Rüdiger T, Gascoyne RD, Jaffe ES, de Jong D, Delabie J, De Wolf-Peeters C, Poppema S, Xerri L, Gisselbrecht C, Wiedenmann S, Müller-Hermelink HK. Workshop on the relationship between nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma and T cell/histiocyte-rich B cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2002;13(Suppl 1):44–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
