Tissue transglutaminase, protein cross-linking and Alzheimer's disease: review and views
- PMID: 18784819
- PMCID: PMC2480529
Tissue transglutaminase, protein cross-linking and Alzheimer's disease: review and views
Abstract
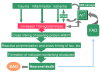
Extensive protein cross-linking and aggregation are some of the most common molecular events in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Both beta-amyloid (Abeta) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, which are extracellular and intracellular proteinaceous aggregates, respectively, contribute to neuronal death and progressive cognitive decline. Although protein cross-linking has been recognized and extensively studied for many years, the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. Recent data indicates that tissue transglutaminase (tTG), which catalyzes the cross-linking of a wide spectrum of proteins including Abeta, tau, alpha-synuclein and neurofilament proteins, may be involved in protein aggregation in AD. Many AD risk factors, such as trauma, inflammation, ischemia and stress, up-regulate tTG protein and activity levels. In this review, we summarize the evidence that tTG plays a role in AD, especially in cross-linking of Abeta, tau, alpha-synuclein and neurofilament proteins. An experimentally testable hypothesis is that tTG may play a central role in AD pathogenesis and that it provides a conceptual link between sporadic and familial AD through a shared pathogenic pathway.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Tissue transglutaminase (tTG, TG2); neurofilament proteins; protein cross-linking; tau; α-synuclein; β-amyloid (Aβ).
Figures
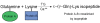



References
-
- Dickson DW. Neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: a perspective from longitudinal clinicopathological studies. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:S21–26. - PubMed
-
- Brookes AJ, St Clair D. Synuclein proteins and Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1994;17:404–405. - PubMed
-
- Bancher C, Brunner C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Jellinger K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wisniewski HM. Accumulation of abnormally phosphorylated tau precedes the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1989;477:90–99. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
