C-MYC rearrangements are frequent in aggressive mature B-Cell lymphoma with atypical morphology
- PMID: 18784824
- PMCID: PMC2480535
C-MYC rearrangements are frequent in aggressive mature B-Cell lymphoma with atypical morphology
Abstract
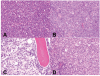
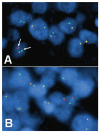
Diagnosis and classification of aggressive mature B-cell lymphoma with atypical morphology remains a challenge. To identify factors that may contribute to the atypical morphology, we selected eight such cases and evaluated their morphologic, immunophenotypic and cytogenetic features and clinical outcomes. The neoplastic cells showed a diffuse monotonous infiltrating pattern with a spectrum of morphology including: 1) L1 lymphoblastic; 2) centroblastic; 3) immunoblastic; and 4) mixed centroblastic and immunoblastic. The lymphoma cells in most cases were positive for CD10 and/or BCL6, and showed BCL2 expression. 6 of 8 cases showed C-MYC rearrangements, and interestingly, all 6 cases demonstrated a proliferation index of < or =90%. 3 of the 6 cases also demonstrated t(14;18). Clinical follow-up indicated that aggressive mature B-cell lymphoma may benefit from more intensified chemotherapeutic regimens used for BL. Our study suggests that aggressive mature B-cell lymphoma with atypical morphology may be another "grey zone lymphoma" lying in the spectrum between Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Keywords: Aggressive mature B-cell lymphoma; Burkitt lymphoma; C-MYC rearrangement; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; grey zone lymphoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transformation of Follicular Lymphoma to a High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma With MYC and BCL2 Translocations and Overlapping Features of Burkitt Lymphoma and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Case Report and Literature Review.Clin Med Insights Blood Disord. 2017 Feb 28;10:1179545X17692544. doi: 10.1177/1179545X17692544. eCollection 2017. Clin Med Insights Blood Disord. 2017. PMID: 28579851 Free PMC article.
-
Double-hit B-cell lymphomas with BCL6 and MYC translocations are aggressive, frequently extranodal lymphomas distinct from BCL2 double-hit B-cell lymphomas.Am J Surg Pathol. 2013 Mar;37(3):323-32. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31826cebad. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23348205
-
The "Burkitt-like" immunophenotype and genotype is rarely encountered in diffuse large B cell lymphoma and high-grade B cell lymphoma, NOS.Virchows Arch. 2021 Sep;479(3):575-583. doi: 10.1007/s00428-021-03050-4. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Virchows Arch. 2021. PMID: 33655392
-
B-cell lymphomas with features intermediate between distinct pathologic entities. From pathogenesis to pathology.Hum Pathol. 2010 May;41(5):621-31. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.10.027. Hum Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20398809 Review.
-
Diagnosis of 'double hit' diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between DLBCL and Burkitt lymphoma: when and how, FISH versus IHC.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014 Dec 5;2014(1):90-9. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2014.1.90. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014. PMID: 25696840 Review.
Cited by
-
MYC Immunohistochemistry Predicts MYC Rearrangements by FISH.Front Oncol. 2017 Sep 21;7:209. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00209. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28983465 Free PMC article.
-
Subcutaneous passage increases cell aggressiveness in a xenograft model of diffuse large B cell lymphoma.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2012 Apr;29(4):339-47. doi: 10.1007/s10585-012-9454-8. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2012. PMID: 22262061
-
Primary sacral non-germinal center type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with MYC translocation: a case report and a review of the literature.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 Aug 15;6(9):1919-28. eCollection 2013. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24040459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of EBV-Positive Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma and the Expression and Clinicopathological Correlations of Some Related Genes.Front Oncol. 2019 Jul 25;9:683. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00683. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31403034 Free PMC article.
-
Precursor B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma with L3 Morphology, Philadelphia Chromosome, MYC Gene Translocation, and Coexpression of TdT and Surface Light Chains: A Case Report.Case Rep Pathol. 2013;2013:679892. doi: 10.1155/2013/679892. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Case Rep Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23533894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blum KA, Lozanski G, Byrd JC. Adult Burkitt leukemia and lymphoma. Blood. 2004;104:3009–3020. - PubMed
-
- Gatter KC, Warnke RA. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors: Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC Press; 2001. pp. 171–174.
-
- Diebold J, Jaffe ES, Raphael M, Warnke RA. Burkitt lymphoma. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors: Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC Press; 2001. pp. 181–184.
-
- Nakamura N, Nakamine H, Tamaru J, Nakamura S, Yoshino T, Ohshima K, Abe M. The distinction between Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma with c-myc rearrangement. Mod Pathol. 2002;15:771–776. - PubMed
-
- Stein H, Hummel M. [Burkitt's and Burkitt-like lymphoma: Molecular definition and value of the World Health Organisation's diagnostic criteria] Pathologe. 2007 [Epub ahead of print] German. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
