Human BLyS facilitates engraftment of human PBL derived B cells in immunodeficient mice
- PMID: 18784835
- PMCID: PMC2527131
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003192
Human BLyS facilitates engraftment of human PBL derived B cells in immunodeficient mice
Abstract
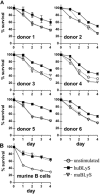
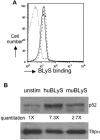
The production of fully immunologically competent humanized mice engrafted with peripheral lymphocyte populations provides a model for in vivo testing of new vaccines, the durability of immunological memory and cancer therapies. This approach is limited, however, by the failure to efficiently engraft human B lymphocytes in immunodeficient mice. We hypothesized that this deficiency was due to the failure of the murine microenvironment to support human B cell survival. We report that while the human B lymphocyte survival factor, B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS/BAFF) enhances the survival of human B cells ex vivo, murine BLyS has no such protective effect. Although human B cells bound both human and murine BLyS, nuclear accumulation of NF-kappaB p52, an indication of the induction of a protective anti-apoptotic response, following stimulation with human BLyS was more robust than that induced with murine BLyS suggesting a fundamental disparity in BLyS receptor signaling. Efficient engraftment of both human B and T lymphocytes in NOD rag1(-/-) Prf1(-/-) immunodeficient mice treated with recombinant human BLyS is observed after adoptive transfer of human PBL relative to PBS treated controls. Human BLyS treated recipients had on average 40-fold higher levels of serum Ig than controls and mounted a de novo antibody response to the thymus-independent antigens in pneumovax vaccine. The data indicate that production of fully immunologically competent humanized mice from PBL can be markedly facilitated by providing human BLyS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Attenuation of apoptosis underlies B lymphocyte stimulator enhancement of humoral immune response.J Exp Med. 2000 Oct 2;192(7):953-64. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.7.953. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 11015437 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of human cell engraftment and development of EBV-related lymphoproliferative disorders in Hu-PBL-scid mice.J Immunol. 2000 Jul 1;165(1):518-27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.1.518. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10861091
-
Generation and characterization of LymphoStat-B, a human monoclonal antibody that antagonizes the bioactivities of B lymphocyte stimulator.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Nov;48(11):3253-65. doi: 10.1002/art.11299. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 14613291
-
Mechanism of BLyS action in B cell immunity.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002 Feb;13(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(01)00025-9. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002. PMID: 11750877 Review.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus: a blissless disease of too much BLyS (B lymphocyte stimulator) protein.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2002 Sep;14(5):522-8. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200209000-00007. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2002. PMID: 12192248 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Humanized Mice to Study the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015 Jul;21(7):1652-73. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000446. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015. PMID: 26035036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arthritogenic T cells drive the recovery of autoantibody-producing B cell homeostasis and the adoptive transfer of arthritis in SCID mice.Int Immunol. 2012 Aug;24(8):507-17. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxs057. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Int Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22518822 Free PMC article.
-
Humanized Mouse Models for Transplant Immunology.Am J Transplant. 2016 Feb;16(2):389-97. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13520. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Am J Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26588186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Newcastle disease virus-like particles as a platform for the development of vaccines for human and agricultural pathogens.Future Virol. 2010 Sep 1;5(5):545-554. doi: 10.2217/fvl.10.50. Future Virol. 2010. PMID: 21339837 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing hematopoietic stem cell yield to develop mice with human immune systems.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:740892. doi: 10.1155/2013/740892. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23509770 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shultz LD, Ishikawa F, Greiner DL. Humanized mice in translational biomedical research. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:118–130. - PubMed
-
- Manz MG. Human-Hemato-Lymphoid-System Mice: Opportunities and Challenges. Immunity. 2007;26:537–541. - PubMed
-
- Di Ianni M, Terenzi A, Falzetti F, Bartoli A, Di Florio S, et al. Homing and survival of thymidine kinase-transduced human T cells in NOD/SCID mice. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002;9:756–761. - PubMed
-
- Goldman JP, Blundell MP, Lopes L, Kinnon C, Di Santo JP, et al. Enhanced human cell engraftment in mice deficient in RAG2 and the common cytokine receptor gamma chain. Br J Haematol. 1998;103:335–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI46629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI041054/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK032520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK32520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI57463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA34196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI046629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI084800/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI041054/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI057463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL77642/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI 041054/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077642/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

