Evidence for the possible involvement of the P2Y(6) receptor in Ca (2+) mobilization and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic islets
- PMID: 18784987
- PMCID: PMC2583206
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-008-9122-2
Evidence for the possible involvement of the P2Y(6) receptor in Ca (2+) mobilization and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic islets
Abstract
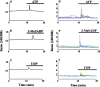
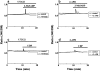
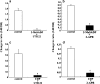
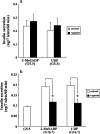
Subtypes of purinergic receptors involved in modulation of cytoplasmic calcium ion concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) and insulin release in mouse pancreatic beta-cells were examined in two systems, pancreatic islets in primary culture and beta-TC6 insulinoma cells. Both systems exhibited some physiological responses such as acetylcholine-stimulated [Ca(2+)](i) rise via cytoplasmic Ca(2+) mobilization. Addition of ATP, ADP, and 2-MeSADP (each 100 microM) transiently increased [Ca(2+)](i) in single islets cultured in the presence of 5.5 mM (normal) glucose. The potent P2Y(1) receptor agonist 2-MeSADP reduced insulin secretion significantly in islets cultured in the presence of high glucose (16.7 mM), whereas a slight stimulation occurred at 5.5 mM glucose. The selective P2Y(6) receptor agonist UDP (200 microM) transiently increased [Ca(2+)](i) and reduced insulin secretion at high glucose, whereas the P2Y(2/4) receptor agonist UTP and adenosine receptor agonist NECA were inactive. [Ca(2+)](i) transients induced by 2-MeSADP and UDP were antagonized by suramin (100 microM), U73122 (2 microM, PLC inhibitor), and 2-APB (10 or 30 microM, IP(3) receptor antagonist), but neither by staurosporine (1 microM, PKC inhibitor) nor depletion of extracellular Ca(2+). The effect of 2-MeSADP on [Ca(2+)](i) was also significantly inhibited by MRS2500, a P2Y(1) receptor antagonist. These results suggested that P2Y(1) and P2Y(6) receptor subtypes are involved in Ca(2+) mobilization from intracellular stores and insulin release in mouse islets. In beta-TC6 cells, ATP, ADP, 2-MeSADP, and UDP transiently elevated [Ca(2+)](i) and slightly decreased insulin secretion at normal glucose, while UTP and NECA were inactive. RT-PCR analysis detected mRNAs of P2Y(1) and P2Y(6), but not P2Y(2) and P2Y(4) receptors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Involvement of P2X receptors in the regulation of insulin secretion, proliferation and survival in mouse pancreatic β-cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28(2):355-66. doi: 10.1159/000331752. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21865744
-
Effect of purinergic agonists and antagonists on insulin secretion from INS-1 cells (insulinoma cell line) and rat pancreatic islets.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002 Jun;80(6):562-8. doi: 10.1139/y02-079. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12117305
-
P2Y receptors mediate Ca2+ signaling in duodenocytes and contribute to duodenal mucosal bicarbonate secretion.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Feb;296(2):G424-32. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90314.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19074643 Free PMC article.
-
[Identification of novel molecules regulating differentiation and hormone secretion and clarification of their functional mechanisms in pancreatic endocrine cells].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Mar;130(3):377-88. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.377. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20190522 Review. Japanese.
-
Pharmacological profiles of cloned mammalian P2Y-receptor subtypes.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Jun;110(3):415-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.08.014. Epub 2005 Oct 28. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16257449 Review.
Cited by
-
Pyrimidine ribonucleotides with enhanced selectivity as P2Y(6) receptor agonists: novel 4-alkyloxyimino, (S)-methanocarba, and 5'-triphosphate gamma-ester modifications.J Med Chem. 2010 Jun 10;53(11):4488-501. doi: 10.1021/jm100287t. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20446735 Free PMC article.
-
The CD39-adenosinergic axis in the pathogenesis of immune and nonimmune diabetes.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:320495. doi: 10.1155/2012/320495. Epub 2012 Oct 14. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23118504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP mediates a negative autocrine signal on stimulus-secretion coupling in mouse pancreatic β-cells.Endocrine. 2019 Feb;63(2):270-283. doi: 10.1007/s12020-018-1731-0. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Endocrine. 2019. PMID: 30229397
-
Purinergic signalling in endocrine organs.Purinergic Signal. 2014 Mar;10(1):189-231. doi: 10.1007/s11302-013-9396-x. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Purinergic Signal. 2014. PMID: 24265070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P2-type purinergic signaling in the regulation of pancreatic β-cell functional plasticity as a promising novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 9;13:1099152. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1099152. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 37065173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1073/pnas.91.10.4343', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.10.4343'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC43781', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC43781/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8183910', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8183910/'}]}
- Ämmälä C, Eliasson L, Bokvist K, Berggren PO, Honkanen RE, Sjöholm Å et al (1994) Activation of protein kinases and inhibition of protein phosphatases play a central role in the regulation of exocytosis in mouse pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4343–4347. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.10.4343 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1136631', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1136631/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2405836', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2405836/'}]}
- Arkhammar P, Hallberg A, Kindmark H, Nilsson T, Rorsman P, Berggren PO (1990) Extracelluar ATP increases cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in clonal insulin-producing RINm5F cells. A mechanism involving direct interaction with both release and refilling of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ pool. Biochem J 265:203–211 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1917920', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1917920/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1364829', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1364829/'}]}
- Bertrand G, Chapal J, Puech R, Loubatières-Mariani MM (1991) Adenosine-5′-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) is a potent agonist at P2 purinoceptors mediating insulin secretion from perfused rat pancreas. Br J Pharmacol 102:627–630 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0167-4889(88)90182-6', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4889(88)90182-6'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2454675', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2454675/'}]}
- Blachier F, Malaisse WJ (1988) Effect of exogenous ATP upon inositol phosphate production, cationic fluxes and insulin release in pancreatic islet cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 970:222–229. doi:10.1016/0167-4889(88)90182-6 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/ddr.430280303', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.430280303'}]}
- Burnstock G (1993) Physiological and pathological roles of purines: an update. Drug Dev Res 28:195–206. doi:10.1002/ddr.430280303
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

