Neuroprotective potential of fasudil mesylate in brain ischemia-reperfusion injury of rats
- PMID: 18785000
- PMCID: PMC11506079
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-008-9308-8
Neuroprotective potential of fasudil mesylate in brain ischemia-reperfusion injury of rats
Abstract
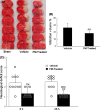
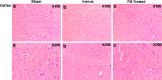
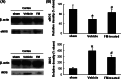
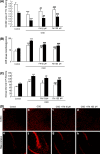
We previously reported that inhibition of Rho-kinase (ROCK) by hydroxyl fasudil improves cognitive deficit and neuronal damage in rats with chronic cerebral ischemia (Huang et al., Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:757-768, 2008). In this study, fasudil mesylate (FM) was investigated for its neuroprotective potential in rats with ischemia following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and reperfusion. The effect of fasudil mesylate was also studied in rat brain cortical and hippocampal slices treated with oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) injury. Gross anatomy showed that cerebral infarct size, measured with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining, was significantly smaller in the FM-treated than in the non-FM-treated ischemic rats. In the brain regions vulnerable to ischemia of ischemic rats, fasudil mesylate was also found to significantly restore the enzyme protein expression level of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), which was decreased in ischemia. However, it remarkably reduced the protein synthesis of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) that was induced by ischemia and reperfusion. In rat brain slices treated with OGD injury, fasudil mesylate increased the neuronal cell viability by 40% for cortex and by 61% for hippocampus, respectively. Finally, in the presence of OGD and fasudil mesylate, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was increased by 50% for cortex and by 58% for hippocampus, compared to OGD only group. In conclusion, our in vivo study showed that fasudil mesylate not only decreased neurological deficit but also reduced cerebral infarct size, possibly and at least partially by augmenting eNOS protein expression and inhibiting iNOS protein expression after ischemia-reperfusion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on brain ischemia/reperfusion damage in diabetic rats.Brain Res. 2015 Mar 30;1602:153-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.01.014. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25601009
-
Inhibition of Rho kinase by fasudil hydrochloride attenuates lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia and reperfusion.Life Sci. 2011 Jan 3;88(1-2):104-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.10.028. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21056587
-
Effects and Mechanism of Action of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase on Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2016 Feb;299(2):246-55. doi: 10.1002/ar.23295. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2016. PMID: 26598930
-
Improvement of cognitive deficit and neuronal damage in rats with chronic cerebral ischemia via relative long-term inhibition of rho-kinase.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008 Aug;28(5):757-68. doi: 10.1007/s10571-007-9157-x. Epub 2007 Jun 7. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 17554619 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Radix Scrophulariae on Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury via MAPK Pathways.Molecules. 2018 Sep 19;23(9):2401. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092401. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30235876 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic potential of Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil derivative FaD-1 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Mar;55(3):725-32. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0411-7. Epub 2014 Sep 16. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25223373
-
EGCG ameliorates the suppression of long-term potentiation induced by ischemia at the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapse in the rat.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Mar;32(2):267-77. doi: 10.1007/s10571-011-9758-2. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22076575 Free PMC article.
-
How can imaging in acute ischemic stroke help us to understand tissue fate in the era of endovascular treatment and cerebroprotection?Neuroradiology. 2022 Sep;64(9):1697-1707. doi: 10.1007/s00234-022-03001-z. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Neuroradiology. 2022. PMID: 35854136 No abstract available.
-
MicroRNAs hsa-miR-618 and hsa-miR-297 Might Modulate the Pleiotropic Effects Exerted by Statins in Endothelial Cells Through the Inhibition of ROCK2 Kinase: in-silico Approach.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 16;8:704175. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.704175. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34485404 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Gene Expression in the Rat Brainstem After Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury and Antioxidant Treatment.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Mar;54(2):1129-1143. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9724-6. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26809461
References
-
- Cohen MM, Pettegrew JW, Kopp SJ, Minshew N, Glonek T (1984) P-31 nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of brain: normoxic and anoxic brain slices. Neurochem Res 9:785–801. doi:10.1007/BF00965666 - PubMed
-
- Davalos A, Toni D, Iweins F, Lesaffre E, Bastianello S, Castillo J (1999) Neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke: potential predictors and associated factors in the European cooperative acute stroke study (ECASS) I. Stroke 30:2631–2636 - PubMed
-
- Dawson VL, Brahmbhatt HP, Mong JA, Dawson TM (1994) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase causes delayed neurotoxicity in primary mixed neuronal-glial cortical cultures. Neuropharmacology 33:1425–1430. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(94)90045-0 - PubMed
-
- De AJ, Cardenas A, Moro MA, Leza JC, Lorenzo P, Lizasoain I (1999) Use of brain slices in the study of pathogenic role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Gen Pharmacol 32:577–581. doi:10.1016/S0306-3623(98)00280-8 - PubMed
-
- Dobashi K, Araki S, Kubo K, Kawagoe R, Yamamoto Y, Shirahata A (2008) Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor inhibits induction of nitric oxide synthase in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Life Sci 82:85–90. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2007.10.013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

