Protective effect of Juzen-taiho-to on hepatocarcinogenesis is mediated through the inhibition of Kupffer cell-induced oxidative stress
- PMID: 18785209
- PMCID: PMC2571981
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.23828
Protective effect of Juzen-taiho-to on hepatocarcinogenesis is mediated through the inhibition of Kupffer cell-induced oxidative stress
Abstract
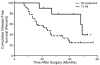
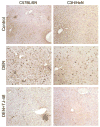
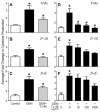
Traditional herbal formulations, such as Juzen-taiho-to (TJ-48), are used extensively in medical practice in Asia even though their mechanism of action remains elusive. This study tested a hypothesis that TJ-48 is protective against hepatocarcinogenesis by impeding Kupffer cell-induced oxidative stress. Forty-eight patients were randomly assigned to receive TJ-48 (n = 10), or no supplementation (n = 38) for up to 6 years after surgical treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In addition, to investigate the mechanism of protective action of TJ-48, diethylnitrosamine-containing water was administered for 22 weeks to male mice that were fed regular chow or TJ-48-containing diet. Liver tumor incidence, cell proliferation, number of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine- or F4/80-positive cells, and cytokine expression were evaluated. Although most of the patients experienced recurrence of HCC, a significantly longer intrahepatic recurrence-free survival was observed in the TJ-48 group. In mice, TJ-48 inhibited the development of liver tumors, reduced oxidative DNA damage, inflammatory cell infiltration and cytokine expression. Administration of TJ-48 improves intrahepatic recurrence-free survival after surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. On the basis of animal experiments, we reason that the protective mechanism of TJ-48 involves inhibition of Kupffer cells. This leads to lower levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidants in liver which may slow down the process of hepatocarcinogenesis and improves hepatic recurrence-free survival in patients with HCC.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of Sho-Saiko-to on hepatocarcinogenesis and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine formation.Hepatology. 2002 May;35(5):1125-33. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.33066. Hepatology. 2002. PMID: 11981762
-
Acyclic retinoid and angiotensin-II receptor blocker exert a combined protective effect against diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in diabetic OLETF rats.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 26;18(1):1164. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5099-6. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30477453 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lycopene and Sho-saiko-to on hepatocarcinogenesis in a rat model of spontaneous liver cancer.Nutr Cancer. 2001;39(1):96-101. doi: 10.1207/S15327914nc391_13. Nutr Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11588908
-
Mode of action of butoxyethanol-induced mouse liver hemangiosarcomas and hepatocellular carcinomas.Toxicol Lett. 2005 Mar 28;156(1):107-15. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.08.012. Toxicol Lett. 2005. PMID: 15705491
-
Inhibitory effects of Japanese herbal medicines sho-saiko-to and juzen-taiho-to on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 22;9(1):e87279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087279. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24466347 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cinnamomum cassia bark in two herbal formulas increases life span in Caenorhabditis elegans via insulin signaling and stress response pathways.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 22;5(2):e9339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009339. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20179756 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Glycyrrhiza glabra (Licorice)-Containing Herbs Alleviating Radiotherapy- and Chemotherapy-Induced Adverse Reactions in Cancer Treatment.Metabolites. 2022 Jun 9;12(6):535. doi: 10.3390/metabo12060535. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35736467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial effects of Kampo products against pneumonia causative bacteria.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 28;19(10):e0312500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312500. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39466752 Free PMC article.
-
Juzentaihoto Failed to Augment Antigen-Specific Immunity but Prevented Deterioration of Patients' Conditions in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer under Personalized Peptide Vaccine.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:981717. doi: 10.1155/2013/981717. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23840274 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic Value of Platelet Count in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Sep;94(37):e1431. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001431. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26376382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inoue H, Seitz HK. Viruses and alcohol in the pathogenesis of primary hepatic carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2001;10:107–10. - PubMed
-
- Kountouras J, Lygidakis NJ. New epidemiological data on liver oncogenesis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47:855–61. - PubMed
-
- Hussain SP, Hofseth LJ, Harris CC. Radical causes of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:276–85. - PubMed
-
- Koike K, Miyoshi H. Oxidative stress and hepatitis C viral infection. Hepatol Res. 2006;34:65–73. - PubMed
-
- De Maria N, Colantoni A, Fagiuoli S, Liu GJ, Rogers BK, Farinati F, Van Thiel DH, Floyd RA. Association between reactive oxygen species and disease activity in chronic hepatitis C. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996;21:291–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

