Improved splicing of adeno-associated viral (AAV) capsid protein-supplying pre-mRNAs leads to increased recombinant AAV vector production
- PMID: 18785816
- PMCID: PMC2940631
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2008.118
Improved splicing of adeno-associated viral (AAV) capsid protein-supplying pre-mRNAs leads to increased recombinant AAV vector production
Abstract
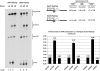
Adeno-associated viral (AAV) capsid proteins, thought to be a rate-limiting step in the production of recombinant AAV (rAAV), are translated from spliced mRNAs. Improvement of the native AAV nonconsensus donor sequence increases splicing yet leaves the relative levels of VP1- and VP2/3-encoding mRNAs unchanged, and thus provides a means to increase delivery of correct ratios of AAV capsid proteins. This effect is independent of the AAV serotype used, and occurs whether the rep and cap genes supplied in trans are on the same or separate expression vectors. In the split-vector system, replacement of the more traditionally used cytomegalovirus promoter with that of the AAV5 P41 promoter allowed for even greater levels of splicing, and together with an improved intron donor, led to a 10- to 15-fold increase in the levels of splicing, rAAV production, and transduction compared with levels achieved by traditional cotransfection methods. Thus, the enhancement of splicing presents a useful method to enhance rAAV production via transient transfection.
Figures
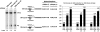
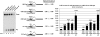

Similar articles
-
Improved Genome Packaging Efficiency of Adeno-associated Virus Vectors Using Rep Hybrids.J Virol. 2021 Sep 9;95(19):e0077321. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00773-21. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34287038 Free PMC article.
-
Intron splicing-mediated expression of AAV Rep and Cap genes and production of AAV vectors in insect cells.Mol Ther. 2008 May;16(5):924-30. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.35. Epub 2008 Mar 18. Mol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18388928
-
Adeno-associated virus 9 (AAV9) viral proteins VP1, VP2, and membrane-associated accessory protein (MAAP) differentially influence in vivo transgene expression.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0168124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01681-24. Epub 2024 Oct 30. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39475275 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of risks related to the use of adeno-associated virus-based vectors.Curr Gene Ther. 2003 Dec;3(6):545-65. doi: 10.2174/1566523034578131. Curr Gene Ther. 2003. PMID: 14683451 Review.
-
The role of the adeno-associated virus capsid in gene transfer.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;437:51-91. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-210-6_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18369962 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improved Genome Packaging Efficiency of Adeno-associated Virus Vectors Using Rep Hybrids.J Virol. 2021 Sep 9;95(19):e0077321. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00773-21. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34287038 Free PMC article.
-
Cre-dependent selection yields AAV variants for widespread gene transfer to the adult brain.Nat Biotechnol. 2016 Feb;34(2):204-9. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3440. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Nat Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26829320 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization strategies and advances in the research and development of AAV-based gene therapy to deliver large transgenes.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Mar;14(3):e1607. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1607. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38488469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding of CCCTC-Binding Factor (CTCF) to the Minute Virus of Mice Genome Is Important for Proper Processing of Viral P4-Generated Pre-mRNAs.Viruses. 2020 Nov 30;12(12):1368. doi: 10.3390/v12121368. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33266080 Free PMC article.
-
Discovering human cell-compatible gene therapy virus variants via optimized screening in mouse models.Cell Prolif. 2024 Mar;57(3):e13565. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13565. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 37864397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atchison R.W. Casto B.C. Hammon W.M. Electron microscopy of adenovirus-associated virus (AAV) in cell cultures. Virology. 1966;29:353–357. - PubMed
-
- Bowles D.E. Rabinowitz J.E. Samulski R.J. The Genus Dependovirus. Hodder Arnold; London: 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

