Archaeal RNA polymerase subunits E and F are not required for transcription in vitro, but a Thermococcus kodakarensis mutant lacking subunit F is temperature-sensitive
- PMID: 18786148
- PMCID: PMC3737576
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06430.x
Archaeal RNA polymerase subunits E and F are not required for transcription in vitro, but a Thermococcus kodakarensis mutant lacking subunit F is temperature-sensitive
Abstract
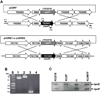
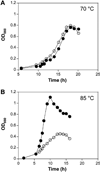
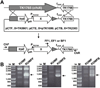
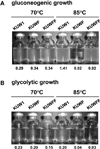
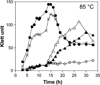
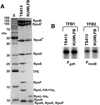
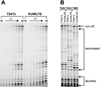
All archaeal genomes encode RNA polymerase (RNAP) subunits E and F that share a common ancestry with the eukaryotic RNAP subunits A43 and A14 (Pol I), Rpb7 and Rpb4 (Pol II), and C25 and C17 (Pol III). By gene replacement, we have isolated archaeal mutants of Thermococcus kodakarensis with the subunit F-encoding gene (rpoF) deleted, but we were unable to isolate mutants lacking the subunit E-encoding gene (rpoE). Wild-type T. kodakarensis grows at temperatures ranging from 60 degrees C to 100 degrees C, optimally at 85 degrees C, and the DeltarpoF cells grew at the same rate as wild type at 70 degrees C, but much slower and to lower cell densities at 85 degrees C. The abundance of a chaperonin subunit, CpkB, was much reduced in the DeltarpoF strain growing at 85 degrees C and increased expression of cpkB, rpoF or rpoE integrated at a remote site in the genome, using a nutritionally regulated promoter, improved the growth of DeltarpoF cells. RNAP preparations purified from DeltarpoF cells lacked subunit F and also subunit E and a transcription factor TFE that co-purifies with RNAP from wild-type cells, but in vitro, this mutant RNAP exhibited no discernible differences from wild-type RNAP in promoter-dependent transcription, abortive transcript synthesis, transcript elongation or termination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An overview of 25 years of research on Thermococcus kodakarensis, a genetically versatile model organism for archaeal research.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2020 Feb;65(1):67-78. doi: 10.1007/s12223-019-00730-2. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2020. PMID: 31286382 Review.
-
Archaeal RNA polymerase arrests transcription at DNA lesions.Transcription. 2017;8(5):288-296. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1324941. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Transcription. 2017. PMID: 28598254 Free PMC article.
-
A Mutant Chaperonin That Is Functional at Lower Temperatures Enables Hyperthermophilic Archaea To Grow under Cold-Stress Conditions.J Bacteriol. 2015 Aug;197(16):2642-52. doi: 10.1128/JB.00279-15. Epub 2015 May 26. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26013483 Free PMC article.
-
Branched-chain polyamine stabilizes RNA polymerase at elevated temperatures in hyperthermophiles.Amino Acids. 2020 Feb;52(2):275-285. doi: 10.1007/s00726-019-02745-y. Epub 2019 May 17. Amino Acids. 2020. PMID: 31101997
-
Prokaryotic sigma factors and their transcriptional counterparts in Archaea and Eukarya.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 May;104(10):4289-4302. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10577-0. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32232532 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription Regulation in Archaea.J Bacteriol. 2016 Jun 27;198(14):1906-1917. doi: 10.1128/JB.00255-16. Print 2016 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27137495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a radical SAM enzyme involved in the synthesis of archaeosine.Nat Chem Biol. 2019 Dec;15(12):1148-1155. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0390-7. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Nat Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31740832
-
Engineering of the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis for Chitin-Dependent Hydrogen Production.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Jul 17;83(15):e00280-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00280-17. Print 2017 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28550062 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of 25 years of research on Thermococcus kodakarensis, a genetically versatile model organism for archaeal research.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2020 Feb;65(1):67-78. doi: 10.1007/s12223-019-00730-2. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2020. PMID: 31286382 Review.
-
The X-ray crystal structure of the euryarchaeal RNA polymerase in an open-clamp configuration.Nat Commun. 2014 Oct 14;5:5132. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6132. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25311937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell SD, Jackson SP. Transcription and translation in Archaea: a mosaic of eukaryal and bacterial features. Trends Microbiol. 1998;6:222–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

