A time and a place for nkx2-1 in interneuron specification and migration
- PMID: 18786351
- PMCID: PMC2632973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.08.017
A time and a place for nkx2-1 in interneuron specification and migration
Abstract
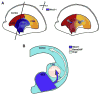
The homeobox transcription factor, Nkx2-1, plays multiple roles during forebrain development. Using restricted genetic ablation of Nkx2-1, in this issue of Neuron, Butt et al. show that Nkx2-1 in telencephalic progenitors regulates interneuron subtype specification, while Nóbrega-Pereira et al. demonstrate that postmitotic Nkx2-1 regulates migration and sorting of interneurons to the striatum or cortex by controlling the expression of the guidance receptor, Neuropilin-2.
Figures
Comment on
-
The requirement of Nkx2-1 in the temporal specification of cortical interneuron subtypes.Neuron. 2008 Sep 11;59(5):722-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.07.031. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18786356 Free PMC article.
-
Postmitotic Nkx2-1 controls the migration of telencephalic interneurons by direct repression of guidance receptors.Neuron. 2008 Sep 11;59(5):733-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.07.024. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18786357 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

