Noncanonical binding of calmodulin to aquaporin-0: implications for channel regulation
- PMID: 18786401
- PMCID: PMC2605016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2008.06.011
Noncanonical binding of calmodulin to aquaporin-0: implications for channel regulation
Abstract
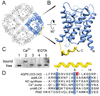
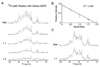
Aquaporins (AQPs) are a family of ubiquitous membrane channels that conduct water across cell membranes. AQPs form homotetramers containing four functional and independent water pores. Aquaporin-0 (AQP0) is expressed in the eye lens, where its water permeability is regulated by calmodulin (CaM). Here we use a combination of biochemical methods and NMR spectroscopy to probe the interaction between AQP0 and CaM. We show that CaM binds the AQP0 C-terminal domain in a calcium-dependent manner. We demonstrate that only two CaM molecules bind a single AQP0 tetramer in a noncanonical fashion, suggesting a form of cooperativity between AQP0 monomers. Based on these results, we derive a structural model of the AQP0/CaM complex, which suggests CaM may be inhibitory to channel permeability by capping the vestibules of two monomers within the AQP0 tetramer. Finally, phosphorylation within AQP0's CaM binding domain inhibits the AQP0/CaM interaction, suggesting a temporal regulatory mechanism for complex formation.
Figures



References
-
- Agre P, Kozono D. Aquaporin water channels: molecular mechanisms for human diseases. FEBS Lett. 2003;555:72–78. - PubMed
-
- Agre P, Sasaki S, Chrispeels MJ. Aquaporins: a family of water channel proteins. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:F461. - PubMed
-
- Alcala J, Lieska N, Maisel H. Protein composition of bovine lens cortical fiber cell membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1975;21:581–595. - PubMed
-
- Arneson ML, Cheng HL, Louis CF. Characterization of the ovine-lens plasma-membrane protein-kinase substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1995;234:670–679. - PubMed
-
- Babu YS, Bugg CE, Cook WJ. Structure of calmodulin refined at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988;204:191–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

