Low-cost optical lifetime assisted ratiometric glutamine sensor based on glutamine binding protein
- PMID: 18786501
- PMCID: PMC2783298
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2008.08.018
Low-cost optical lifetime assisted ratiometric glutamine sensor based on glutamine binding protein
Abstract
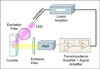
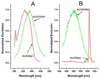
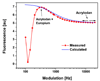
Here we report a reagentless fluorescence sensing technique for glutamine in the submicromolar range based on the glutamine binding protein (QBP). The S179C mutant is labeled with the short-lived acrylodan (lifetime<5ns) and the long-lived tris(dibenzoylmethane) mono(5-amino-1,10-phenanthroline)europium(III) (lifetime > 300 micros) at the -SH and the N-terminal positions, respectively. In the presence of glutamine the fluorescence of acrylodan is quenched, while the fluorescence of europium complex remains constant. In this report we describe an innovative technique, the so called lifetime assisted ratiometric sensing to discriminate the two fluorescence signals using minimal optics and power requirements. This method exploits the large difference between the fluorescence lifetimes of the two fluorophores to isolate the individual fluorescence from each other by alternating the modulation frequency of the excitation light between 300 Hz and 10 kHz. The result is a ratiometric optical method that does not require expensive and highly attenuating band pass filters for each of the dyes, but only one long pass filter for both. Thus, the signal to noise ratio is enhanced, and at the same time, the optical setup is simplified. The end product is a simple sensing device suitable for low-cost applications such as point-of-care diagnostics or in-the-field analysis.
Figures
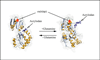


Similar articles
-
Reagentless optical sensing of glutamine using a dual-emitting glutamine-binding protein.Anal Biochem. 2003 Mar 15;314(2):199-205. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(02)00586-9. Anal Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12654305
-
Fatty acid sensor for low-cost lifetime-assisted ratiometric sensing using a fluorescent fatty acid binding protein.Anal Biochem. 2005 Oct 1;345(1):133-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2005.07.030. Anal Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16137630
-
Optical determination of glutamine using a genetically engineered protein.Anal Biochem. 2001 Apr 1;291(1):89-95. doi: 10.1006/abio.2001.4998. Anal Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11262160 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
On the design of low-cost fluorescent protein biosensors.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2009;116:143-57. doi: 10.1007/10_2008_39. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19347267 Review.
-
The concept of λ-ratiometry in fluorescence sensing and imaging.J Fluoresc. 2010 Sep;20(5):1099-128. doi: 10.1007/s10895-010-0644-y. Epub 2010 Apr 1. J Fluoresc. 2010. PMID: 20358283 Review.
Cited by
-
Long wavelength fluorescence lifetime standards for front-face fluorometry.J Fluoresc. 2010 Mar;20(2):435-40. doi: 10.1007/s10895-009-0565-9. Epub 2009 Dec 2. J Fluoresc. 2010. PMID: 19953311 Free PMC article.
-
Environmentally sensitive fluorescent sensors based on synthetic peptides.Sensors (Basel). 2010;10(4):3126-44. doi: 10.3390/s100403126. Epub 2010 Mar 31. Sensors (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22319290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A luminescence lifetime assisted ratiometric fluorimeter for biological applications.Rev Sci Instrum. 2009 Dec;80(12):124302. doi: 10.1063/1.3264106. Rev Sci Instrum. 2009. PMID: 20059156 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering the Signal Resolution of a Paper-Based Cell-Free Glutamine Biosensor with Genetic Engineering, Metabolic Engineering, and Process Optimization.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 12;24(10):3073. doi: 10.3390/s24103073. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793927 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive technique for measuring transdermal glucose with a fluorescent biosensor.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Nov;410(27):7249-7260. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1336-8. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 30171282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Labow BI, Souba WW. Glutamine. World J. Surg. 2000;24:1503–1513. - PubMed
-
- Curi R, Lagranha CJ, Doi SQ, Sellitti DF, Procopio J, Pithon-Curi TC, Corless M, Newsholme P. Molecular mechanisms of glutamine action. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005;204:392–401. - PubMed
-
- Lieth E, LaNoue KF, Berkich DA, Xu B, Ratz M, Taylor C, Hutson SM. Nitrogen shuttling between neurons and glial cells during glutamate synthesis. J. Neurochem. 2001;76:1712–1723. - PubMed
-
- Dumaswala UJ, Zhuo L, Mahajan S, Nair PN, Shertzer HG, Dibello P, Jacobsen DW. Glutathione protects chemokine scavenging and antioxidative defense functions in human RBCs. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;280:C867–C873. - PubMed
-
- Matés JM, Pérez-Gómez C, Núñez de Castro I, Asenjo M, Márquez J. Glutamine and its relationship with intracellular redox status, oxidative stress and cell proliferation/death. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2002;34:439–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

