Plasma membrane glutathione transporters and their roles in cell physiology and pathophysiology
- PMID: 18786560
- PMCID: PMC2716123
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.004
Plasma membrane glutathione transporters and their roles in cell physiology and pathophysiology
Abstract
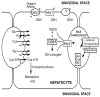
Reduced glutathione (GSH) is critical for many cellular processes, and both its intracellular and extracellular concentrations are tightly regulated. Intracellular GSH levels are regulated by two main mechanisms: by adjusting the rates of synthesis and of export from cells. Some of the proteins responsible for GSH export from mammalian cells have recently been identified, and there is increasing evidence that these GSH exporters are multispecific and multifunctional, regulating a number of key biological processes. In particular, some of the multidrug resistance-associated proteins (Mrp/Abcc) appear to mediate GSH export and homeostasis. The Mrp proteins mediate not only GSH efflux, but they also export oxidized glutathione derivatives (e.g., glutathione disulfide (GSSG), S-nitrosoglutathione (GS-NO), and glutathione-metal complexes), as well as other glutathione S-conjugates. The ability to export both GSH and oxidized derivatives of GSH, endows these transporters with the capacity to directly regulate the cellular thiol-redox status, and therefore the ability to influence many key signaling and biochemical pathways. Among the many processes that are influenced by the GSH transporters are apoptosis, cell proliferation, and cell differentiation. This report summarizes the evidence that Mrps contribute to the regulation of cellular GSH levels and the thiol-redox state, and thus to the many biochemical processes that are influenced by this tripeptide.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander RL, Bates DJ, Wright MW, King SB, Morrow CS. Modulation of nitrated lipid signaling by multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1): glutathione conjugation and MRP1-mediated efflux inhibit nitrolinoleic acid-induced, PPARgamma-dependent transcription activation. Biochemistry. 2006;45:7889–7896. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CP, Tsai JM, Meek WE, Liu RM, Tang Y, Forman HJ, Reynolds CP. Depletion of glutathione by buthionine sulfoxine is cytotoxic for human neuroblastoma cell lines via apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 1999;246 (1):183–192. - PubMed
-
- Aracena P, Sánchez G, Donoso P, Hamilton SL, Hidalgo C. S-Glutathionylation decreases Mg2+ inhibition and S-nitrosylation enhances Ca2+ activation of RyR1 channels. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(44):42927–42935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

