Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus RTA activates the processivity factor ORF59 through interaction with RBP-Jkappa and a cis-acting RTA responsive element
- PMID: 18786687
- PMCID: PMC5868747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.08.011
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus RTA activates the processivity factor ORF59 through interaction with RBP-Jkappa and a cis-acting RTA responsive element
Abstract
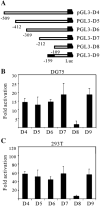
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV8) displays two life modes, latency and lytic reactivation in the infected host cells which are equally important for virus mediated pathogenesis. During latency only a small number of genes are expressed. Under specific conditions, KSHV can undergo lytic replication with the production of viral progeny. One immediate-early gene RTA, encoded by open reading frame 50 of KSHV, has been shown to play a critical role in switching the viral latency to lytic reactivation. Over-expression of RTA from a heterologous promoter is sufficient for driving KSHV lytic replication which results in production of viral progeny. In the present study, we show that RTA can activate the expression of the ORF59 which encodes the processivity factor essential for DNA replication during lytic reactivation. We also show that RTA regulates ORF59 promoter through interaction with RBP-Jkappa as well as a cis-acting RTA responsive element within the promoter. In the context of KSHV infected cells, the upregulation of ORF59 is a direct response to RTA expression. Taken together, our findings provide new evidence to explain the mechanism by which RTA can regulate its downstream gene ORF59, further increasing our understanding of the biology of KSHV lytic replication.
Figures
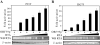
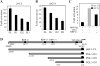

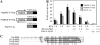
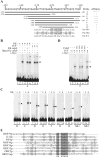

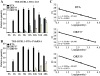
Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Direct RTA Targets Reveals Key Host Factors for Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Reactivation.J Virol. 2019 Feb 19;93(5):e01978-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01978-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30541837 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded latency-associated nuclear antigen inhibits lytic replication by targeting Rta: a potential mechanism for virus-mediated control of latency.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(12):6585-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6585-6594.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15163750 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of RBP-Jkappa in activation of the K8 delayed-early promoter of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by ORF50/RTA.Virology. 2007 Mar 1;359(1):19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.09.032. Epub 2006 Oct 18. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17055026 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV reactivation and novel implications of protein isomerization on lytic switch control.Viruses. 2015 Jan 12;7(1):72-109. doi: 10.3390/v7010072. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25588053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of KSHV lytic reactivation by viral and cellular factors.Curr Opin Virol. 2022 Feb;52:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.004. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Curr Opin Virol. 2022. PMID: 34872030 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The RBP-Jκ binding sites within the RTA promoter regulate KSHV latent infection and cell proliferation.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Jan;8(1):e1002479. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002479. Epub 2012 Jan 12. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22253595 Free PMC article.
-
Sp3 Transcription Factor Cooperates with the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF50 Protein To Synergistically Activate Specific Viral and Cellular Gene Promoters.J Virol. 2020 Aug 31;94(18):e01143-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01143-20. Print 2020 Aug 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32641483 Free PMC article.
-
Abortive lytic reactivation of KSHV in CBF1/CSL deficient human B cell lines.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(5):e1003336. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003336. Epub 2013 May 16. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23696732 Free PMC article.
-
Viral pseudo-enzyme facilitates KSHV lytic replication via suppressing PFAS-mediated RTA deamidation.Virol Sin. 2025 Jun;40(3):340-348. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2025.04.005. Epub 2025 Apr 12. Virol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40228741 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of alternative transcripts encoding the essential murine gammaherpesvirus lytic transactivator RTA.J Virol. 2014 May;88(10):5474-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03110-13. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24574412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AuCoin DP, Colletti KS, Cei SA, Papouskova I, Tarrant M, Pari GS. Amplification of the Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8 lytic origin of DNA replication is dependent upon a cis-acting AT-rich region and an ORF50 response element and the trans-acting factors ORF50 (K-Rta) and K8 (K-bZIP) Virology. 2004;318(2):542–555. - PubMed
-
- Buonaguro FM, Tornesello ML, Beth-Giraldo E, Hatzakis A, Mueller N, Downing R, Biryamwaho B, Sempala SD, Giraldo G. Herpesvirus-like DNA sequences detected in endemic, classic, iatrogenic and epidemic Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) biopsies. Int J Cancer. 1996;65(1):25–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

