Limbic and cortical information processing in the nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 18786735
- PMCID: PMC2884964
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.08.002
Limbic and cortical information processing in the nucleus accumbens
Abstract
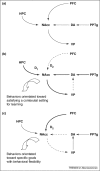
The nucleus accumbens regulates goal-directed behaviors by integrating information from limbic structures and the prefrontal cortex. Here, we review recent studies in an attempt to provide an integrated view of the control of information processing in the nucleus accumbens in terms of the regulation of goal-directed behaviors and how disruption of these functions might underlie the pathological states in drug addiction and other psychiatric disorders. We propose a model that could account for the results of several studies investigating limbic-system interactions in the nucleus accumbens and their modulation by dopamine and provide testable hypotheses for how these might relate to the pathophysiology of major psychiatric disorders.
Figures
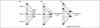
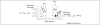
References
-
- Groenewegen HJ, et al. Convergence and segregation of ventral striatal inputs and outputs. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999;877:49–63. - PubMed
-
- Grace AA. Gating of information flow within the limbic system and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2000;31:330–341. - PubMed
-
- Cassaday HJ, et al. Electrolytic lesions to nucleus accumbens core and shell have dissociable effects on conditioning to discrete and contextual cues in aversive and appetitive procedures respectively. Behav. Brain Res. 2005;160:222–235. - PubMed
-
- Cardinal RN, et al. Impulsive choice induced in rats by lesions of the nucleus accumbens core. Science. 2001;292:2499–2501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

