Inhibition of gluconeogenesis in primary hepatocytes by stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) through a c-Src/Akt-dependent signaling pathway
- PMID: 18786922
- PMCID: PMC2576540
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M803698200
Inhibition of gluconeogenesis in primary hepatocytes by stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) through a c-Src/Akt-dependent signaling pathway
Abstract
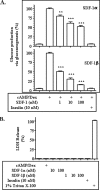
Hepatic gluconeogenesis is elevated in diabetes and a major contributor to hyperglycemia. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) is a chemokine and an activator of Akt. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that SDF-1 suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis through Akt. Our results from isolated primary hepatocytes show that SDF-1alpha and SDF-1beta inhibited glucose production via gluconeogenesis and reduced transcript levels of key gluconeogenic genes glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK). Additionally, SDF-1alpha and SDF-1beta both inhibited activation of the PEPCK promoter. In examining the mechanism by which SDF-1 inhibits gluconeogenesis, we found that SDF-1 promoted phosphorylation of Akt, FoxO1, and c-Src, but did not activate insulin receptor substrate-1-like insulin. Blockade of Akt activation by LY294002, FoxO1 translocation by constitutively nuclear FoxO1 mutant, or c-Src activation by the chemical inhibitor PP2, respectively, blunted SDF-1 suppression of gluconeogenesis. Finally, our results show that knocking down the level of SDF-1 receptor CXCR4 mRNA blocked SDF-1 suppression of gluconeogenesis. Together, our results demonstrate that SDF-1 is capable of inhibiting gluconeogenesis in primary hepatocytes through a signaling pathway distinct from the insulin signaling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Irisin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases glycogen synthesis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice and hepatocytes.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Nov;129(10):839-50. doi: 10.1042/CS20150009. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26201094
-
Suppression of hepatic glucose production by human neutrophil alpha-defensins through a signaling pathway distinct from insulin.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 2;283(18):12056-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801033200. Epub 2008 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18347011 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-19a mediates gluconeogenesis by targeting PTEN in hepatocytes.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Mar;17(3):3967-3971. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8312. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29257352
-
IRS2 and PTP1B: Two opposite modulators of hepatic insulin signalling.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2011 Jul;117(3):105-15. doi: 10.3109/13813455.2011.557386. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21401320 Review.
-
CREB and FoxO1: two transcription factors for the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis.BMB Rep. 2013 Dec;46(12):567-74. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.12.248. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 24238363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of palmitate on hepatic insulin resistance are mediated by NADPH Oxidase 3-derived reactive oxygen species through JNK and p38MAPK pathways.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 24;285(39):29965-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.128694. Epub 2010 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20647313 Free PMC article.
-
Soraphen A, an inhibitor of acetyl CoA carboxylase activity, interferes with fatty acid elongation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Mar 1;81(5):649-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.12.014. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21184748 Free PMC article.
-
Abl kinases are required for invadopodia formation and chemokine-induced invasion.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 17;285(51):40201-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.147330. Epub 2010 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20937825 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic autophagy is suppressed in the presence of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: inhibition of FoxO1-dependent expression of key autophagy genes by insulin.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 6;284(45):31484-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.033936. Epub 2009 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19758991 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin is a stronger inducer of insulin resistance than hyperglycemia in mice with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27090-100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.016675. Epub 2009 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19654321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Accili, D. (2004) Diabetes 53 1633-1642 - PubMed
-
- Whiteman, E. L., Cho, H., and Birnbaum, M. J. (2002) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 13 444-451 - PubMed
-
- Ono, H., Shimano, H., Katagiri, H., Yahagi, N., Sakoda, H., Onishi, Y., Anai, M., Ogihara, T., Fujishiro, M., Viana, A. Y., Fukushima, Y., Abe, M., Shojima, N., Kikuchi, M., Yamada, N., Oka, Y., and Asano, T. (2003) Diabetes 52 2905-2913 - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto, M., Pocai, A., Rossetti, L., Depinho, R. A., and Accili, D. (2007) Cell Metab. 6 208-216 - PubMed
-
- Gross, D. N., van den Heuvel, A. P., and Birnbaum, M. J. (2008) Oncogene 27 2320-2336 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

