The expression of GPIHBP1, an endothelial cell binding site for lipoprotein lipase and chylomicrons, is induced by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
- PMID: 18787041
- PMCID: PMC2582544
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0146
The expression of GPIHBP1, an endothelial cell binding site for lipoprotein lipase and chylomicrons, is induced by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
Erratum in
- Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Dec;22(12):2766
Abstract
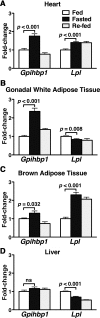
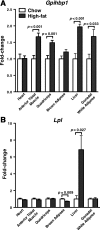
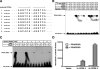
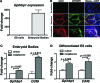
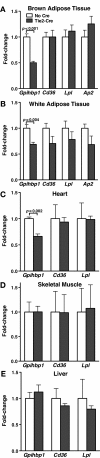
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 (GPIHBP1), a protein in the lymphocyte antigen 6 (Ly-6) family, plays a key role in the lipolytic processing of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. GPIHBP1 binds lipoprotein lipase and chylomicrons and is expressed along the luminal surface of microvascular endothelial cells. Lipolysis is known to be regulated by metabolic factors and is controlled at multiple levels, including the number of LPL binding sites on capillaries. Here, we tested the possibility that GPIHBP1 expression could be regulated by dietary perturbations and by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). Gpihbp1 transcript levels in the heart and in brown and white adipose tissue increased with fasting and returned toward baseline after refeeding. A PPARgamma agonist increased Gpihbp1 expression in adipose tissue, heart, and skeletal muscle, whereas PPARalpha and PPARdelta agonists had no effect. Gpihbp1 was expressed in endothelial cells of embryoid bodies generated from mouse embryonic stem cells, and Gpihbp1 expression in embryoid bodies was up-regulated by a PPARgamma agonist. Sequences upstream from exon 1 of Gpihbp1 contain a strong PPAR binding site, and that site exhibited activity in a luciferase reporter assay. Gpihbp1 transcript levels in brown and white adipose tissue were lower in endothelial cell PPARgamma knockout mice than in littermate control mice, suggesting that PPARgamma regulates Gpihbp1 expression in vivo. We conclude that GPIHBP1 is regulated by dietary factors and by PPARgamma.
Figures
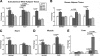
Similar articles
-
A novel NanoBiT-based assay monitors the interaction between lipoprotein lipase and GPIHBP1 in real time.J Lipid Res. 2020 Apr;61(4):546-559. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D119000388. Epub 2020 Feb 6. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 32029511 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 plays a critical role in the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons.Cell Metab. 2007 Apr;5(4):279-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.02.002. Cell Metab. 2007. PMID: 17403372 Free PMC article.
-
GPIHBP1 and lipolysis: an update.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009 Jun;20(3):211-6. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32832ac026. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009. PMID: 19369870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GPIHBP1: an endothelial cell molecule important for the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2007 Aug;18(4):389-96. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e3281527914. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2007. PMID: 17620854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylation of Asn-76 in mouse GPIHBP1 is critical for its appearance on the cell surface and the binding of chylomicrons and lipoprotein lipase.J Lipid Res. 2008 Jun;49(6):1312-21. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700593-JLR200. Epub 2008 Mar 13. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18340083 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 and the intravascular processing of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins.J Intern Med. 2012 Dec;272(6):528-40. doi: 10.1111/joim.12003. Epub 2012 Nov 1. J Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 23020258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelium as a gatekeeper of fatty acid transport.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Feb;25(2):99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24315207 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of lipoprotein lipase and GPIHBP1 in mouse pancreas: effects of diet and leptin deficiency.BMC Physiol. 2012 Nov 27;12:14. doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-12-14. BMC Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23186339 Free PMC article.
-
An upstream enhancer regulates Gpihbp1 expression in a tissue-specific manner.J Lipid Res. 2019 Apr;60(4):869-879. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M091322. Epub 2018 Dec 31. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30598475 Free PMC article.
-
A novel NanoBiT-based assay monitors the interaction between lipoprotein lipase and GPIHBP1 in real time.J Lipid Res. 2020 Apr;61(4):546-559. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D119000388. Epub 2020 Feb 6. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 32029511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beigneux AP, Davies BS, Gin P, Weinstein MM, Farber E, Qiao X, Peale F, Bunting S, Walzem RL, Wong JS, Blaner WS, Ding ZM, Melford K, Wongsiriroj N, Shu X, de Sauvage F, Ryan RO, Fong LG, Bensadoun A, Young SG 2007 Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 plays a critical role in the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons. Cell Metab 5:279–291 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goldberg IJ 1996 Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis. J Lipid Res 37:693–707 - PubMed
-
- Mead JR, Irvine SA, Ramji DP 2002 Lipoprotein lipase: structure, function, regulation, and role in disease. J Mol Med 80:753–769 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087228/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL66621/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01HL090553-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL090553/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL66088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 HL066088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066621/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL66600/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066600/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

