A refined two-hybrid system reveals that SCF(Cdc4)-dependent degradation of Swi5 contributes to the regulatory mechanism of S-phase entry
- PMID: 18787112
- PMCID: PMC2567208
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806253105
A refined two-hybrid system reveals that SCF(Cdc4)-dependent degradation of Swi5 contributes to the regulatory mechanism of S-phase entry
Abstract
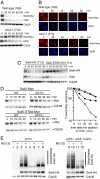
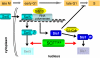
Ubiquitin-dependent degradation is implicated in various cellular regulatory mechanisms. The SCF(Cdc4) (Skp1, Cullin/Cdc53, and the F-box protein Cdc4) complex is an ubiquitin ligase complex that acts as a regulator of cell cycle, signal transduction, and transcription. These regulatory mechanisms are not well defined because of the difficulty in identifying the interaction between ubiquitin ligases and their substrates. To identify substrates of the yeast SCF(Cdc4) ubiquitin ligase complex, we refined the yeast two-hybrid system to allow screening Cdc4-substrate interactions under conditions of substrate stabilization, and identified Swi5 as a substrate of the SCF(Cdc4) complex. Swi5 is the transcriptional activator of Sic1, the inhibitor of S phase cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). We showed that Swi5 is indeed ubiquitinated and degraded through the SCF(Cdc4) complex. Furthermore, the SCF(Cdc4)-dependent degradation of Swi5 was required to terminate SIC1 transcription at early G(1) phase, which ensured efficient entry into S phase: Hyperaccumulation of Sic1 was noted in cells expressing stabilized Swi5, and expression of stabilized Swi5 delayed S phase entry, which was dominantly suppressed by SIC1 deletion. These findings indicate that the SCF(Cdc4) complex regulates S phase entry not only through degradation of Sic1, but also through degradation of Swi5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transferable domain in the G(1) cyclin Cln2 sufficient to switch degradation of Sic1 from the E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF(Cdc4) to SCF(Grr1).Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(13):4463-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.13.4463-4476.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12052857 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of a Fbw7-Skp1-cyclin E complex: multisite-phosphorylated substrate recognition by SCF ubiquitin ligases.Mol Cell. 2007 Apr 13;26(1):131-43. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.02.022. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17434132
-
Skp, Cullin, F-box (SCF)-Met30 and SCF-Cdc4-Mediated Proteolysis of CENP-A Prevents Mislocalization of CENP-A for Chromosomal Stability in Budding Yeast.PLoS Genet. 2020 Feb 7;16(2):e1008597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008597. eCollection 2020 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32032354 Free PMC article.
-
Multisite phosphorylation and the countdown to S phase.Cell. 2001 Dec 28;107(7):819-22. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00620-1. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11779457 Review.
-
Genetically engineered mouse models for functional studies of SKP1-CUL1-F-box-protein (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligases.Cell Res. 2013 May;23(5):599-619. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.44. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23528706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Degradation of Ndd1 by APC/C(Cdh1) generates a feed forward loop that times mitotic protein accumulation.Nat Commun. 2015 May 11;6:7075. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8075. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25959309
-
Lessons from fungal F-box proteins.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 May;8(5):677-95. doi: 10.1128/EC.00386-08. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 19286981 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Global analysis of phosphorylation and ubiquitylation cross-talk in protein degradation.Nat Methods. 2013 Jul;10(7):676-82. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2519. Epub 2013 Jun 9. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23749301 Free PMC article.
-
In silico analysis of a Skp1 protein homolog from the human pathogen E. histolytica.J Parasit Dis. 2022 Dec;46(4):998-1010. doi: 10.1007/s12639-022-01523-0. Epub 2022 Jul 23. J Parasit Dis. 2022. PMID: 36457763 Free PMC article.
-
Cul8/Rtt101 forms a variety of protein complexes that regulate DNA damage response and transcriptional silencing.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 26;285(13):9858-9867. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082107. Epub 2010 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20139071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Willems A, Schwab M, Tyers M. A hitchhiker's guide to the cullin ubiquitin ligases: SCF and its kin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1695:133–170. - PubMed
-
- Schwob E, Böhm T, Mendenhall MD, Nasmyth K. The B-type cyclin kinase inhibitor p40SIC1 controls the G1 to S transition in S cerevisiae. Cell. 1994;79:233–244. - PubMed
-
- Verma R, et al. Phosphorylation of Sic1p by G1 Cdk required for its degradation and entry into S phase. Science. 1997;278:455–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

