Integrating the MicroRNome into the study of lung disease
- PMID: 18787215
- PMCID: PMC2615660
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200807-1042PP
Integrating the MicroRNome into the study of lung disease
Abstract
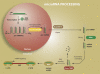
Over the last 15 years, investigators have identified small noncoding RNAs as regulators of gene expression. One type of noncoding RNAs are termed microRNAs (miRNAs). miRNAs are evolutionary conserved, approximately 22-nucleotide single-stranded RNAs that target genes by inducing mRNA degradation or by inhibiting translation. miRNAs are implicated in many critical cellular processes, including apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation. Furthermore, it is estimated that miRNAs may be responsible for regulating the expression of nearly one-third of the human genome. Despite the identification of greater than 500 mature miRNAs, very little is known about their biological functions and functional targets. In the last 5 years, researchers have increasingly focused on the functional relevance and role that miRNAs play in the pathogenesis of human disease. miRNAs are known to be important in solid organ and hematological malignancies, heart disease, as potential modulators of the immune response, and organ development. It is anticipated that miRNA analysis will emerge as an important complement to proteomic and genomic studies to further our understanding of disease pathogenesis. Despite the application of genomics and proteomics to the study of human lung disease, few studies have examined miRNA expression. This perspective is not meant to be an exhaustive review of miRNA biology but will provide an overview of both miRNA biogenesis and our current understanding of the role of miRNAs in lung disease as well as a perspective on the importance of integrating this analysis as a tool for identifying and understanding the biological pathways in lung-disease pathogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of Lung Cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2009 Aug;4(8):1028-34. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a99c77. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19474765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease--pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapeutics.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep 14;18(34):4629-34. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4629. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23002331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: Emerging Regulators of Immune-Mediated Diseases.Scand J Immunol. 2012 Feb;75(2):129-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02650.x. Scand J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21988491 Review.
-
The Emerging Role of MitomiRs in the Pathophysiology of Human Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:123-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26663182
-
Protocols for the Analysis of microRNA Expression, Biogenesis, and Function in Immune Cells.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019 Sep;126(1):e78. doi: 10.1002/cpim.78. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31483103 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systems biology of interstitial lung diseases: integration of mRNA and microRNA expression changes.BMC Med Genomics. 2011 Jan 17;4:8. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21241464 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs profiling in murine models of acute and chronic asthma: a relationship with mRNAs targets.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 28;6(1):e16509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016509. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21305051 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic control of gene expression in the lung.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 May 15;183(10):1295-301. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201010-1579PP. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21596832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary MicroRNA Changes Alter Angiogenesis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Lung Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 16;9(7):830. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070830. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356894 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous miRNA Sponges.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2257:91-104. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1170-8_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34432275
References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Chu CY, Rana TM. Small RNAs: regulators and guardians of the genome. J Cell Physiol 2007;213:412–419. - PubMed
-
- Mertens-Talcott SU, Chintharlapalli S, Li X, Safe S. The oncogenic microRNA-27a targets genes that regulate specificity protein transcription factors and the G2-M checkpoint in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2007;67:11001–11011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

