Regulation of Wnt protein secretion and its role in gradient formation
- PMID: 18787559
- PMCID: PMC2572129
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2008.167
Regulation of Wnt protein secretion and its role in gradient formation
Abstract
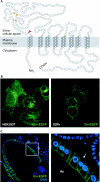
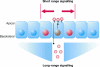
In metazoans, many developmental and disease-related processes are mediated by Wnt proteins, which are secreted by specific cells to regulate cellular programmes in the surrounding tissue. Although the Wnt-induced signal-transduction cascades are well studied, little is known about how Wnts are secreted. The discovery of Porcupine, an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident acyltransferase, led to closer inspection of the secretory routes of Wnts, and the analysis of Wnt secretion has become an exciting new area of research. Wnt post-translational modifications, interaction partners and subcellular localizations now indicate that Wnt release is tightly regulated. In this review, we summarize recent advances in the field of Wnt secretion and discuss the possibility that separate pathways might regulate the release of lipid-linked morphogens for short-range and long-range signalling.
Figures


References
-
- Banziger C, Soldini D, Schutt C, Zipperlen P, Hausmann G, Basler K (2006) Wntless, a conserved membrane protein dedicated to the secretion of Wnt proteins from signaling cells. Cell 125: 509–522 - PubMed
-
- Bartscherer K, Pelte N, Ingelfinger D, Boutros M (2006) Secretion of Wnt ligands requires Evi, a conserved transmembrane protein. Cell 125: 523–533 - PubMed
-
- Belenkaya TY, Wu Y, Tang X, Zhou B, Cheng L, Sharma YV, Yan D, Selva EM, Lin X (2008) The retromer complex influences Wnt secretion by recycling wntless from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. Dev Cell 14: 120–131 - PubMed
-
- Burke R, Nellen D, Bellotto M, Hafen E, Senti KA, Dickson BJ, Basler K (1999) Dispatched, a novel sterol-sensing domain protein dedicated to the release of cholesterol-modified hedgehog from signaling cells. Cell 99: 803–815 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

