The alliance of sphingosine-1-phosphate and its receptors in immunity
- PMID: 18787560
- PMCID: PMC2600775
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2400
The alliance of sphingosine-1-phosphate and its receptors in immunity
Abstract
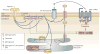
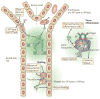
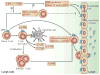
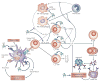
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a biologically active metabolite of plasma-membrane sphingolipids that is essential for immune-cell trafficking. Its concentration is increased in many inflammatory conditions, such as asthma and autoimmunity. Much of the immune function of S1P results from the engagement of a family of G-protein-coupled receptors (S1PR1-S1PR5). Recent findings on the role of S1P in immunosurveillance, the discovery of regulatory mechanisms in S1P-mediated immune-cell trafficking and new advances in understanding the mechanism by which S1P affects immune-cell function indicate that the alliance between S1P and its receptors has a fundamental role in immunity.
Figures
References
-
- Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:139–150. This is a comprehensive overview of the regulation and function of sphingolipid metabolism in cellular function. - PubMed
-
- Rivera J, Olivera A. Src family kinases and lipid mediators in control of allergic inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2007;217:255–268. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez T, Hla T. Structural and functional characteristics of S1P receptors. J Cell Biochem. 2004;92:913–922. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, et al. The immune modulator FTY720 targets sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:21453–21457. - PubMed
-
- Matloubian M, et al. Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature. 2004;427:355–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

