Expression and trafficking of the gamma subunit of Na,K-ATPase in hypertonically challenged IMCD3 cells
- PMID: 18787637
- PMCID: PMC2532601
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.08018
Expression and trafficking of the gamma subunit of Na,K-ATPase in hypertonically challenged IMCD3 cells
Abstract
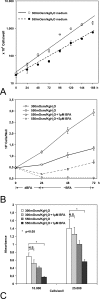
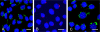
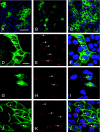
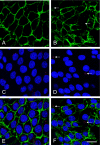
The gamma subunit (FXYD2) of Na,K-ATPase is an important regulator of the sodium pump. In this investigation we have analysed the trafficking of gamma to the plasma membrane in cultures of inner medullary collecting duct cells (IMCD3) following acute hypertonic challenge and brefeldin A (BFA) treatment. Following hypertonic challenging for 24 hr immunofluorescence labeling revealed initial co-localization of the gamma subunit and 58K Golgi protein in the cytoplasm, but no co-localization of alpha1 and Golgi protein. Exposure of the challenged cells to BFA prevented the subsequent incorporation of gamma into the basolateral plasma membrane. The gamma subunit instead remained in cytoplasmic vesicles while cell proliferation and cell viability decreased simultaneously. Following removal of BFA from the hypertonic medium the IMCD3 cells recovered with distinct expression of gamma in the basolateral membrane. The alpha1 subunit was only marginally influenced by BFA. The results demonstrate that the gamma subunit trafficks to the plasma membrane via the Golgi apparatus, despite the absence of a signal sequence. The results also suggest that the gamma and alpha subunits do not traffic together to the plasma membrane, and that the gamma and alpha subunit have different turnover rates during these experimental conditions.
Keywords: FXYD2; Golgi apparatus; brefeldin A; confocal microscopy; hypertonicity.
Figures
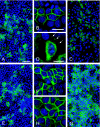
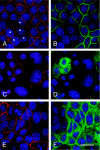
Similar articles
-
Beneficial Renal and Pancreatic Phenotypes in a Mouse Deficient in FXYD2 Regulatory Subunit of Na,K-ATPase.Front Physiol. 2016 Mar 7;7:88. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00088. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27014088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The gamma-subunit of Na-K-ATPase is incorporated into plasma membranes of mouse IMCD3 cells in response to hypertonicity.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Apr;288(4):F650-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00162.2004. Epub 2004 Nov 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15572522
-
Silencing and overexpression of the gamma-subunit of Na-K-ATPase directly affect survival of IMCD3 cells in response to hypertonic stress.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):F1142-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00077.2006. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16804105
-
Chloride, not sodium, stimulates expression of the gamma subunit of Na/K-ATPase and activates JNK in response to hypertonicity in mouse IMCD3 cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 27;100(11):6428-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1130871100. Epub 2003 May 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12746499 Free PMC article.
-
The gamma subunit of Na/K-ATPase: an exceptional, small transmembrane protein.Front Biosci. 2005 Sep 1;10:2604-10. doi: 10.2741/1724. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15970522 Review.
Cited by
-
FXYD2c plays a potential role in modulating Na(+)/K (+)-ATPase activity in HK-2 cells upon hypertonic challenge.J Membr Biol. 2014 Jan;247(1):93-105. doi: 10.1007/s00232-013-9615-y. Epub 2013 Nov 21. J Membr Biol. 2014. PMID: 24258619
-
Beneficial Renal and Pancreatic Phenotypes in a Mouse Deficient in FXYD2 Regulatory Subunit of Na,K-ATPase.Front Physiol. 2016 Mar 7;7:88. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00088. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27014088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FXYD2 and Na,K-ATPase expression in isolated human proximal tubular cells: disturbed upregulation on renal hypomagnesemia?J Membr Biol. 2009 Oct;231(2-3):117-24. doi: 10.1007/s00232-009-9210-4. Epub 2009 Oct 29. J Membr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19865785 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional control of Na,K-ATPase activity and cell growth by a splice variant of FXYD2 protein with modified mRNA.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 20;286(20):18290-300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.241901. Epub 2011 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21460224 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of noradrenaline-induced stimulation of Na-K ATPase activity in the rat brain: implications on REM sleep deprivation-induced increase in brain excitability.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Mar;336(1-2):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0260-9. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19823772 Review.
References
-
- Ackermann U., Geering K. Mutual dependence of Na,K-ATPase α- and β-subunits for correct posttranslational processing and intracellular transport. FEBS. 1990;269:105–108. - PubMed
-
- Barzilay E., Ben-Califa N., Hirschberg K., Neuman D. Uncoupling of brefeldin A-mediated coatomer protein complex-1 dissociation from Golgi redistribution. Traffic. 2005;6:794–802. - PubMed
-
- Bloom G. S., Brashear T. A. A novel 58-kDa protein associates with the Golgi apparatus and microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:16083–16092. - PubMed
-
- Bowen J. W. Regulation of Na+-K+-ATPase expression in cultured renal cells by incubation in hypertonic medium. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1992;262:C845–C853. - PubMed

