BDNF protein levels are decreased in transformed lymphoblasts from lithium-responsive patients with bipolar disorder
- PMID: 18787660
- PMCID: PMC2527719
BDNF protein levels are decreased in transformed lymphoblasts from lithium-responsive patients with bipolar disorder
Abstract
Objective: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key factor in neuroplasticity and has been implicated in the affective disorders; studies have demonstrated elevated BDNF in patients taking lithium and other mood stabilizers. The objective of our study was to analyze BDNF in lithium-responsive patients with bipolar disorder (BD) to further understand the role of BDNF in the pathophysiology of BD.
Methods: Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, we measured transformed B lymphocytes for BDNF protein.
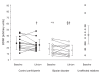
Results: BDNF levels were 36% lower in lymphoblasts from patients with BD (n = 12), compared with matched control participants (n = 13), and 55% lower when compared with their unaffected relatives (n = 14). Lithium significantly decreased BDNF levels in patients with BD and healthy control participants, although BDNF levels remained lower (33%) in the BD group posttreatment.
Conclusion: Decreased BDNF may constitute part of the pathophysiologic process of BD in a lithium-responsive subgroup of individuals with this disease. A compensatory mechanism protecting the genetically predisposed unaffected relatives from phenotypic expression of BD is suggested.
Objectif: Le facteur neurotrophique dérivé du cerveau (FNDC) joue un rôle clé dans la neuroplasticité et est mis en cause dans des troubles de l'affectivité. Des études ont démontré des concentrations élevées de FNDC chez les patients qui prenaient du lithium et d'autres thymorégulateurs. Nous voulions analyser la concentration de FNDC chez les patients atteints d'un trouble bipolaire (TB) répondant au lithium afin de comprendre davantage le rôle du FNDC dans la pathophysiologie du TB.
Méthodes: Nous avons mesuré par dosage immunoenzymatique les lymphocytes B transformés pour déterminer les protéines dans le FNDC.
Résultats: Les concentrations de FNDC étaient plus faibles de 36 % dans les lymphoblastes provenant de patients atteints d'un TB (n = 12) que dans ceux des participants témoins jumelés (n = 13), et 55 % moins élevés que chez les membres de leur parenté non atteints (n = 14). Le lithium a réduit considérablement les concentrations de FNDC chez les patients atteints de TB et les participants témoins en bonne santé, même si elles sont demeurées plus faibles (33 %) chez les patients atteints de TB après le traitement.
Conclusion: La diminution des concentrations de FNDC peut constituer un élément du processus pathophysiologique du TB chez un sous-groupe d'individus atteints de la maladie qui répondent au lithium. On pense qu'un mécanisme compensatoire protège contre l'expression phénotypique du TB les patients apparentés non touchés qui sont génétiquement prédisposés.
Keywords: bipolar disorder; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; lithium.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alterations in BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor) and GDNF (glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor) serum levels in bipolar disorder: The role of lithium.J Affect Disord. 2014 Sep;166:193-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.05.012. Epub 2014 May 22. J Affect Disord. 2014. PMID: 25012431
-
Association studies of the BDNF and the NTRK2 gene polymorphisms with prophylactic lithium response in bipolar patients.Pharmacogenomics. 2008 Nov;9(11):1595-603. doi: 10.2217/14622416.9.11.1595. Pharmacogenomics. 2008. PMID: 19018715 Clinical Trial.
-
Cognitive function and serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with bipolar disorder.Bipolar Disord. 2009 Sep;11(6):663-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5618.2009.00733.x. Bipolar Disord. 2009. PMID: 19689509
-
Peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a biomarker in bipolar disorder: a meta-analysis of 52 studies.BMC Med. 2015 Nov 30;13:289. doi: 10.1186/s12916-015-0529-7. BMC Med. 2015. PMID: 26621529 Free PMC article.
-
[Predictors of prophylactic response to lithium].Encephale. 2008 Sep;34(4):394-9. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2007.05.002. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Encephale. 2008. PMID: 18922242 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Pharmacogenomics of mood stabilizers in the treatment of bipolar disorder.Hum Genomics Proteomics. 2010 Aug 3;2010:159761. doi: 10.4061/2010/159761. Hum Genomics Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20981231 Free PMC article.
-
Towards the clinical implementation of pharmacogenetics in bipolar disorder.BMC Med. 2014 May 30;12:90. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-12-90. BMC Med. 2014. PMID: 24885933 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium response in bipolar disorder correlates with improved cell viability of patient derived cell lines.Sci Rep. 2020 May 4;10(1):7428. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64202-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32366893 Free PMC article.
-
EGR3 Immediate Early Gene and the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Bipolar Disorder.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Feb 5;12:15. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00015. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29459824 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels among Euthymic Adolescents with Bipolar Disorder Type I.Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2016 Sep;53(3):267-271. doi: 10.5152/npa.2015.8832. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2016. PMID: 28373806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alda M. The phenotypic spectra of bipolar disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2004;14(Suppl 2):S94-9. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with bipolar disorder (revision). Am J Psychiatry 2002;159(4 Suppl):1-50. - PubMed
-
- Yatham LN, Kennedy SH, O'Donovan C, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder: consensus and controversies. Bipolar Disord 2005;7(Suppl 3):5-69. - PubMed
-
- Grof P, Alda M, Grof E, et al. Lithium response and genetics of affective disorders. J Affect Disord 1994;32:85-95. - PubMed
-
- Turecki G, Grof P, Cavazzoni P, et al. Evidence for a role of phospholipase C-gamma1 in the pathogenesis of bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 1998;3:534-8. - PubMed
