Development of the vertebral morphogenetic field in the mouse: interactions between Crossveinless-2 and Twisted Gastrulation
- PMID: 18789316
- PMCID: PMC2647368
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.08.019
Development of the vertebral morphogenetic field in the mouse: interactions between Crossveinless-2 and Twisted Gastrulation
Abstract
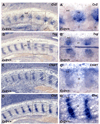
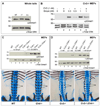
Crossveinless-2 (Cv2), Twisted Gastrulation (Tsg) and Chordin (Chd) are components of an extracellular biochemical pathway that regulates Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) activity during dorso-ventral patterning of Drosophila and Xenopus embryos, the formation of the fly wing, and mouse skeletogenesis. Because the nature of their genetic interactions remained untested in the mouse, we generated a null allele for Cv2 which was crossed to Tsg and Chd mutants to obtain Cv2; Tsg and Cv2; Chd compound mutants. We found that Cv2 is essential for skeletogenesis as its mutation caused the loss of multiple bone structures and posterior homeotic transformation of the last thoracic vertebra. During early vertebral development, Smad1 phosphorylation in the intervertebral region was decreased in the Cv2 mutant, even though CV2 protein is normally located in the future vertebral bodies. Because Cv2 mutation affects BMP signaling at a distance, this suggested that CV2 is involved in the localization of the BMP morphogenetic signal. Cv2 and Chd mutations did not interact significantly. However, mutation of Tsg was epistatic to all CV2 phenotypes. We propose a model in which CV2 and Tsg participate in the generation of a BMP signaling morphogenetic field during vertebral formation in which CV2 serves to concentrate diffusible Tsg/BMP4 complexes in the vertebral body cartilage.
Figures





References
-
- Bachiller D, Klingensmith J, Kemp C, Belo JA, Anderson RM, May SR, McMahon JA, McMahon AP, Harland RM, Rossant J, De Robertis EM. The organizer factors Chordin and Noggin are required for mouse forebrain development. Nature. 2000;403:658–661. - PubMed
-
- Bachiller D, Klingensmith J, Shneyder N, Tran U, Anderson R, Rossant J, De Robertis EM. The role of Chordin/BMP signals in mammalian pharyngeal development and DiGeorge syndrome. Development. 2003;130:3567–3578. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Zvi D, Ben-Zion S, Fainsod A, Barkai N. Scaling of the BMP activation gradient in Xenopus embryos. Nature. 2008;453:1205–1211. - PubMed
-
- Bier E. Intriguing extracellular regulation of BMP signaling. Dev. Cell. 2008;15:176–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

