A randomized trial of near versus distance activities while patching for amblyopia in children aged 3 to less than 7 years
- PMID: 18789533
- PMCID: PMC2615691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.06.031
A randomized trial of near versus distance activities while patching for amblyopia in children aged 3 to less than 7 years
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether performing near activities while patching for amblyopia enhances improvement in visual acuity.
Design: Randomized clinical trial.
Participants: A total of 425 children, aged 3 to <7 years, with amblyopia (20/40-20/400) that was caused by anisometropia, strabismus, or both, and that persisted after treatment with spectacles.
Methods: Children were randomized to 2 hours of patching per day with near activities or 2 hours of patching per day with distance activities. Instruction sheets describing common near and distance activities were given to the parents. Study visits were scheduled at 2, 5, 8, and 17 weeks. In weeks without a visit, weekly telephone calls were made to the parent to monitor and encourage compliance during the first 8 weeks.
Main outcome measure: Masked assessment of visual acuity by isolated crowded HOTV optotypes at 8 weeks.
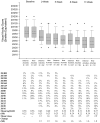
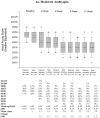
Results: At 8 weeks, improvement in amblyopic eye visual acuity averaged 2.6 lines in the distance activities group and 2.5 lines in the near activities group (mean difference in acuity between groups, adjusted for baseline acuity, 0.0 lines 95% confidence interval, -0.3 to 0.3). The 2 groups also appeared statistically similar at the 2-, 5-, and 17-week visits. At the 17-week examination, children with severe amblyopia improved a mean of 3.6 lines with 2 hours of daily patching.
Conclusions: Performing common near activities does not improve visual acuity outcome when treating anisometropic, strabismic, or combined amblyopia with 2 hours of daily patching. Children with severe amblyopia may respond to 2 hours of daily patching.
Figures


Comment in
-
Amblyopia treatment.Ophthalmology. 2009 Aug;116(8):1588-9; author reply 1589. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.03.036. Ophthalmology. 2009. PMID: 19651315 No abstract available.
References
-
- Francois J, James M. Comparative study of amblyopic treatment. Am Orthopt J. 1955;5:61–4. - PubMed
-
- Callahan WP, Berry D. The value of visual stimulation during contact and direct occlusion. Am Orthopt J. 1968;18:73–4. - PubMed
-
- von Noorden GK, Springer F, Romano P, Parks M. Home therapy for amblyopia. Am Orthopt J. 1970;20:46–50. - PubMed
-
- Watson PG, Sanac AS, Pickering MS. A comparison of various methods of treatment of amblyopia: a block study. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK. 1985;104:319–28. - PubMed
-
- Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. A randomized trial of prescribed patching regimens for treatment of severe amblyopia in children. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:2075–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

