The CCN family of proteins: structure-function relationships
- PMID: 18789696
- PMCID: PMC2683937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2008.07.006
The CCN family of proteins: structure-function relationships
Abstract
The CCN proteins are key signalling and regulatory molecules involved in many vital biological functions, including cell proliferation, angiogenesis, tumourigenesis and wound healing. How these proteins influence such a range of functions remains incompletely understood but is probably related to their discrete modular nature and a complex array of intra- and inter-molecular interactions with a variety of regulatory proteins and ligands. Although certain aspects of their biology can be attributed to the four individual modules that constitute the CCN proteins, recent results suggest that some of their biological functions require cooperation between modules. Indeed, the modular structure of CCN proteins provides important insight into their structure-function relationships.
Figures



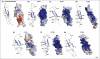
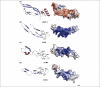
References
-
- Bork P. The modular architecture of a new family of growth regulators related to connective tissue growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1993;327:125–130. - PubMed
-
- Lau L.F., Lam S.C. The CCN family of angiogenic regulators: the integrin connection. Exp. Cell Res. 1999;248:44–57. - PubMed
-
- Brigstock D.R. The connective tissue growth factor/cysteine-rich 61/nephroblastoma overexpressed (CCN) family. Endocr. Rev. 1999;20:189–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

