Characterization of rotavirus specific B cells and their relation with serological memory
- PMID: 18789807
- PMCID: PMC2582161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.08.004
Characterization of rotavirus specific B cells and their relation with serological memory
Abstract
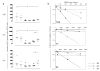
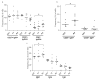
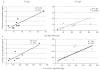
We quantified circulating total, rotavirus (RV) and Tetanus toxin (TT) memory B cells (mBc) in healthy adults using a limiting dilution assay (LDA) and a flow cytometry assay (FCA) that permit evaluation of both CD27+ and CD27- mBc. RV mBc were enriched in the CD27-, IgG+ and in the CD27+, IgM+ subsets. The numbers of RV mBc were higher by FCA than by LDA and results of the two assays did not correlate. TT IgGmBc and RV IgA mBc determined by FCA and by LDA correlated with TT plasma IgG and RV plasma IgA, respectively. The mean ratio of specific mBc/mug/ml of the corresponding plasma immunoglobulin was lower for TT IgG than for RV IgA mBc. Our studies contribute to understand the relationship between circulating mBc and serological memory, and enhance our capacity to develop better correlates of protection against RV disease.
Figures


References
-
- Amanna IJ, Carlson NE, Slifka MK. Duration of humoral immunity to common viral and vaccine antigens. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(19):1903–15. - PubMed
-
- Angel J, Franco MA, Greenberg HB. Rotavirus vaccines: recent developments and future considerations. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5(7):529–39. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi NL, Traggiai E, Lanzavecchia A. Maintenance of serological memory by polyclonal activation of human memory B cells. Science. 2002;298(5601):2199–202. - PubMed
-
- Blutt SE, Conner ME. Rotavirus: to the gut and beyond! Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2007;23(1):39–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

